Parvalbumin cell ablation of NMDA-R1 causes increased resting network excitability with associated social and self-care deficits
- PMID: 24525709
- PMCID: PMC4023157
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2014.7
Parvalbumin cell ablation of NMDA-R1 causes increased resting network excitability with associated social and self-care deficits
Abstract
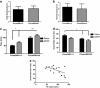
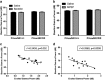
NMDA-receptor (NMDAR) hypofunction is strongly implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Several convergent lines of evidence suggest that net excitation propagated by impaired NMDAR signaling on GABAergic interneurons may be of particular interest in mediating several aspects of schizophrenia. However, it is unclear which behavioral domains are governed by a net increase of excitation and whether modulating downstream GABAergic signaling can reverse neural and thus behavioral deficits. The current study determines the selective contributions of NMDAR dysfunction on PV-containing interneurons to electrophysiological, cognitive, and negative-symptom-related behavioral phenotypes of schizophrenia using mice with a PVcre-NR1flox-driven ablation of NR1 on PV-containing interneurons. In addition, we assessed the efficacy of one agent that directly modulates GABAergic signaling (baclofen) and one agent that indirectly modifies NMDAR-mediated signaling through antagonism of mGluR5 receptors (2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl) pyridine (MPEP)). The data indicate that loss of NMDAR function on PV interneurons impairs self-care and sociability while increasing N1 latency and baseline gamma power, and reducing induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation. Baclofen normalized baseline gamma power without corresponding effects on behavior. MPEP further increased N1 latency and reduced social behavior in PVcre/NR1+/+ mice. These two indices were negatively correlated before and following MPEP such that as N1 latency increases, sociability decreases. This finding suggests a predictive role for N1 latency with respect to social function. Although previous data suggest that MPEP may be beneficial for core features of autism spectrum disorders, current data suggest that such effects require intact function of NMDAR on PV interneurons.
Figures



References
-
- Arnold LE, Aman MG, Martin A, Collier-Crespin A, Vitiello B, Tierney E, et al. Assessment in multisite randomized clinical trials of patients with autistic disorder: the Autism RUPP Network. Research Units on Pediatric Psychopharmacology. J Autism Dev Disord. 2000;30:99–111. - PubMed
-
- Burket JA, Herndon AL, Winebarger EE, Jacome LF, Deutsch SI. Complex effects of mGluR5 antagonism on sociability and stereotypic behaviors in mice: possible implications for the pharmacotherapy of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Res Bull. 2011;86:152–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

