Next-generation active immunization approach for synucleinopathies: implications for Parkinson's disease clinical trials
- PMID: 24525765
- PMCID: PMC4034750
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-014-1256-4
Next-generation active immunization approach for synucleinopathies: implications for Parkinson's disease clinical trials
Abstract
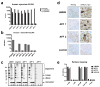
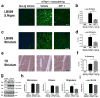
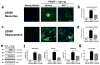
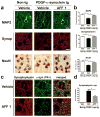
Immunotherapeutic approaches are currently in the spotlight for their potential as disease-modifying treatments for neurodegenerative disorders. The discovery that α-synuclein (α-syn) can transmit from cell to cell in a prion-like fashion suggests that immunization might be a viable option for the treatment of synucleinopathies. This possibility has been bolstered by the development of next-generation active vaccination technology with short peptides-AFFITOPEs(®) (AFF)- that do not elicit an α-syn-specific T cell response. This approach allows for the production of long term, sustained, more specific, non-cross reacting antibodies suitable for the treatment of synucleinopathies, such as Parkinson's disease (PD). In this context, we screened a large library of peptides that mimic the C-terminus region of α-syn and discovered a novel set of AFF that identified α-syn oligomers. Next, the peptide that elicited the most specific response against α-syn (AFF 1) was selected for immunizing two different transgenic (tg) mouse models of PD and Dementia with Lewy bodies, the PDGF- and the mThy1-α-syn tg mice. Vaccination with AFF 1 resulted in high antibody titers in CSF and plasma, which crossed into the CNS and recognized α-syn aggregates. Active vaccination with AFF 1 resulted in decreased accumulation of α-syn oligomers in axons and synapses, accompanied by reduced degeneration of TH fibers in the caudo-putamen nucleus and by improvements in motor and memory deficits in both in vivo models. Clearance of α-syn involved activation of microglia and increased anti-inflammatory cytokine expression, further supporting the efficacy of this novel active vaccination approach for synucleinopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors Markus Mandler, Harald Weninger, Radmila Santic, Stefanie Meindl, Benjamin Vigl, Oskar Smrzka and Achim Schneeberger are employees of AFFiRiS, the company that commercialize the AFFITOPEs® described in the manuscript. The author Frank Mattner is co-founder of AFFiRiS. The authors Elvira Valera, Edward Rockenstein, Christina Patrick, Anthony Adame and Eliezer Masliah declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

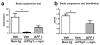





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS057096/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS076411/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062962/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057096/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG018440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG022074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS044233/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS044233/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043384/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS047303/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG18440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG022074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

