EZH2: not EZHY (easy) to deal
- PMID: 24526064
- PMCID: PMC4020974
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0546
EZH2: not EZHY (easy) to deal
Abstract
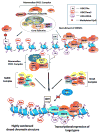
Seminal discoveries have established that epigenetic modifications are important for driving tumor progression. Polycomb group (PcG) proteins are highly conserved epigenetic effectors that maintain, by posttranslational modification of histones, the silenced state of genes involved in critical biologic processes, including cellular development, stem cell plasticity, and tumor progression. PcG proteins are found in two multimeric protein complexes called Polycomb repressive complexes: PRC1 and PRC2. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), catalytic core subunit of PRC2, epigenetically silences several tumor-suppressor genes by catalyzing the trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27, which serves as a docking site for DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases. Evidence suggests that overexpression of EZH2 is strongly associated with cancer progression and poor outcome in disparate cancers, including hematologic and epithelial malignancies. The regulatory circuit and molecular cues causing EZH2 deregulation vary in different cancer types. Therefore, this review provides a comprehensive overview on the oncogenic role of EZH2 during tumorigenesis and highlights the multifaceted role of EZH2, as either a transcriptional activator or repressor depending on the cellular context. Additional insight is provided on the recent understanding of the causes and consequences of EZH2 overexpression in specific cancer types. Finally, evidence is discussed on how EZH2 has emerged as a promising target in anticancer therapy and the prospects for targeting EZH2 without affecting global methylation status. Thus, a better understanding of the complex epigenetic regulatory network controlling EZH2 expression and target genes facilitates the design of novel therapeutic interventions.
©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nature reviews Genetics. 2002;3:415–28. - PubMed
-
- Sims RJ, Reinberg D. Is there a code embedded in proteins that is based on post-translational modifications? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:815–20. - PubMed
-
- Schuettengruber B, Cavalli G. Recruitment of polycomb group complexes and their role in the dynamic regulation of cell fate choice. Development (Cambridge, England) 2009;136:3531–42. - PubMed
-
- Lewis EB. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. 1978;276:565–70. - PubMed
-
- Schuettengruber B, Chourrout D, Vervoort M, Leblanc B, Cavalli G. Genome regulation by polycomb and trithorax proteins. Cell. 2007;128:735–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

