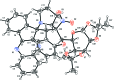
6a-Nitro-6-(2,2,7,7-tetra-methyl-tetra-hydro-3aH-bis-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-b:4',5'-d]pyran-5-yl)-6a,6b,7,8,9,11a-hexa-hydro-6H-spiro-[chromeno[3,4-a]pyrrolizine-11,11'-indeno-[1,2-b]quinoxaline]
- PMID: 24526984
- PMCID: PMC3914082
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813032467
6a-Nitro-6-(2,2,7,7-tetra-methyl-tetra-hydro-3aH-bis-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-b:4',5'-d]pyran-5-yl)-6a,6b,7,8,9,11a-hexa-hydro-6H-spiro-[chromeno[3,4-a]pyrrolizine-11,11'-indeno-[1,2-b]quinoxaline]
Abstract
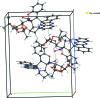
In the title compound, C39H38N4O8, the quinoxaline and indene subunits are essentially planar, with maximum deviations of 0.071 (2) and 0.009 (2) Å, respectively. The indeno-quinoxaline system forms a dihedral angle of 72.81 (3)° with the chromenopyrrolizine system. The two dioxolane rings, as well as the pyran ring of the chromeno group and the terminal pyrrolizine, each adopt an envelope conformation with O and C as flap atoms. The central pyrrolizine ring adopts a twisted conformation. Intra-molecular C-H⋯O and C-H⋯N hydrogen bonds occur. The crystal structure exhibits C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, and is further stablized by C-H⋯π inter-actions, forming a two-dimensional network along the bc plane.
Figures
References
-
- Bruker (2004). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bruker (2008). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
-
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous