Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on amygdaloid histone acetylation and neuropeptide Y expression: a role in anxiety-like and alcohol-drinking behaviours
- PMID: 24528596
- PMCID: PMC4140694
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145714000054
Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on amygdaloid histone acetylation and neuropeptide Y expression: a role in anxiety-like and alcohol-drinking behaviours
Abstract
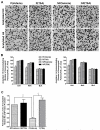
Recent studies have demonstrated the involvement of epigenetic mechanisms in psychiatric disorders, including alcoholism. Here, we investigated the effects of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, trichostatin A (TSA) on amygdaloid HDAC-induced histone deacetylation and neuropeptide Y (NPY) expression and on anxiety-like and alcohol-drinking behaviours in alcohol-preferring (P) and -non-preferring (NP) rats. It was found that P rats displayed higher anxiety-like and alcohol-drinking behaviours, higher amygdaloid nuclear, but not cytosolic, HDAC activity, which was associated with increased HDAC2 protein levels and deficits in histone acetylation and NPY expression in the central (CeA) and medial nucleus of amygdala (MeA), as compared to NP rats. TSA treatment attenuated the anxiety-like and alcohol-drinking behaviours, with concomitant reductions in amygdaloid nuclear, but not cytosolic HDAC activity, and HDAC2, but not HDAC4, protein levels in the CeA and MeA of P rats, without effect in NP rats. TSA treatment also increased global histone acetylation (H3-K9 and H4-K8) and NPY expression in the CeA and MeA of P, but not in NP rats. Histone H3 acetylation within the NPY promoter was also innately lower in the amygdala of P rats compared with NP rats; which was normalized by TSA treatment. Voluntary ethanol intake in P, but not NP rats, produced anxiolytic effects and decreased the HDAC2 levels and increased histone acetylation in the CeA and MeA. These results suggest that higher HDAC2 expression-related deficits in histone acetylation may be involved in lower NPY expression in the amygdala of P rats, and operative in controlling anxiety-like and alcohol-drinking behaviours.
Figures




References
-
- Badia-Elder NE, Stewart RB, Powrozek TA, Roy KF, Murphy JM, Li T-K. Effect of neuropeptide Y (NPY) on oral ethanol intake in Wistar, alcohol-preferring (P), and -non preferring (NP) rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001;25:386–390. - PubMed
-
- Bell RL, Rodd ZA, Lumeng L, Murphy JM, McBride WJ. The alcohol-preferring P rat and animal models of excessive alcohol drinking. Addict Biol. 2006;11:270–288. - PubMed
-
- Broide RS, Redwine JM, Aftahi N, Young W, Bloom FE, Winrow CJ. Distribution of histone deacetylases 1-11 in the rat brain. J Mol Neurosci. 2007;31:47–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

