3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration
- PMID: 24529628
- PMCID: PMC4065717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.01.064
3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration
Abstract
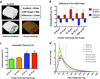
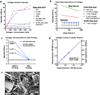
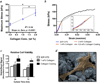
Low temperature 3D printing of calcium phosphate scaffolds holds great promise for fabricating synthetic bone graft substitutes with enhanced performance over traditional techniques. Many design parameters, such as the binder solution properties, have yet to be optimized to ensure maximal biocompatibility and osteoconductivity with sufficient mechanical properties. This study tailored the phosphoric acid-based binder solution concentration to 8.75 wt% to maximize cytocompatibility and mechanical strength, with a supplementation of Tween 80 to improve printing. To further enhance the formulation, collagen was dissolved into the binder solution to fabricate collagen-calcium phosphate composites. Reducing the viscosity and surface tension through a physiologic heat treatment and Tween 80, respectively, enabled reliable thermal inkjet printing of the collagen solutions. Supplementing the binder solution with 1-2 wt% collagen significantly improved maximum flexural strength and cell viability. To assess the bone healing performance, we implanted 3D printed scaffolds into a critically sized murine femoral defect for 9 weeks. The implants were confirmed to be osteoconductive, with new bone growth incorporating the degrading scaffold materials. In conclusion, this study demonstrates optimization of material parameters for 3D printed calcium phosphate scaffolds and enhancement of material properties by volumetric collagen incorporation via inkjet printing.
Keywords: Bone regeneration; Calcium phosphate scaffold; Collagen; Three dimensional printing; Tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest and nothing to disclose.
Figures
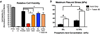

References
-
- De Long WG, Jr, Einhorn TA, Koval K, McKee M, Smith W, Sanders R, et al. Bone grafts and bone graft substitutes in orthopaedic trauma surgery. A critical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(3):649–658. - PubMed
-
- Kurien T, Pearson RG, Scammell BE. Bone graft substitutes currently available in orthopaedic practice: the evidence for their use. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(5):583–597. - PubMed
-
- Seitz H, Rieder W, Irsen S, Leukers B, Tille C. Three-dimensional printing of porous ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;74(2):782–788. - PubMed
-
- Fierz FC, Beckmann F, Huser M, Irsen SH, Leukers B, Witte F, et al. The morphology of anisotropic 3D-printed hydroxyapatite scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2008;29(28):3799–3806. - PubMed
-
- Igawa K, Mochizuki M, Sugimori O, Shimizu K, Yamazawa K, Kawaguchi H, et al. Tailor-made tricalcium phosphate bone implant directly fabricated by a three-dimensional ink-jet printer. J Artif Organs. 2006;9(4):234–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

