New insights into cancer immunoediting and its three component phases--elimination, equilibrium and escape
- PMID: 24531241
- PMCID: PMC4388310
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.01.004
New insights into cancer immunoediting and its three component phases--elimination, equilibrium and escape
Abstract
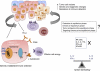
The principles of cancer immunoediting have set the foundations for understanding the dual host-protective and tumour sculpting actions of immunity on cancer and establishing the basis for novel individualized cancer immunotherapies. During cancer immunoediting, the host immune system shapes tumour fate in three phases through the activation of innate and adaptive immune mechanisms. In the first phase, Elimination, transformed cells are destroyed by a competent immune system. Sporadic tumour cells that manage to survive immune destruction may then enter an Equilibrium phase where editing occurs. The Escape phase represents the third and final phase of the process, where immunologically sculpted tumours begin to grow progressively, become clinically apparent and establish an immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment. This review focuses on important recent developments that have enhanced our understanding of each phase of the cancer immunoediting process, summarizes the discovery of new predictive and prognostic biomarkers and discusses development of novel and objectively effective cancer immunotherapies.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Shankaran V, Ikeda H, Bruce AT, White JM, Swanson PE, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumor development and shape tumor immunogenicity. Nature. 2001;410:1107–1111. - PubMed
-
- Dunn GP, Koebel CM, Schreiber RD. Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:836–848. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. 2011;331:1565–1570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

