p38 MAPK signaling underlies a cell-autonomous loss of stem cell self-renewal in skeletal muscle of aged mice
- PMID: 24531379
- PMCID: PMC4070883
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3465
p38 MAPK signaling underlies a cell-autonomous loss of stem cell self-renewal in skeletal muscle of aged mice
Abstract
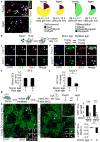
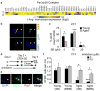
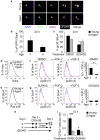
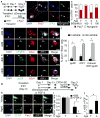
Skeletal muscle aging results in a gradual loss of skeletal muscle mass, skeletal muscle function and regenerative capacity, which can lead to sarcopenia and increased mortality. Although the mechanisms underlying sarcopenia remain unclear, the skeletal muscle stem cell, or satellite cell, is required for muscle regeneration. Therefore, identification of signaling pathways affecting satellite cell function during aging may provide insights into therapeutic targets for combating sarcopenia. Here, we show that a cell-autonomous loss in self-renewal occurs via alterations in fibroblast growth factor receptor-1, p38α and p38β mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in satellite cells from aged mice. We further demonstrate that pharmacological manipulation of these pathways can ameliorate age-associated self-renewal defects. Thus, our data highlight an age-associated deregulation of a satellite cell homeostatic network and reveal potential therapeutic opportunities for the treatment of progressive muscle wasting.
Figures

Comment in
-
Rejuvenating aged muscle stem cells.Nat Med. 2014 Mar;20(3):234-5. doi: 10.1038/nm.3499. Nat Med. 2014. PMID: 24603790 No abstract available.
References
-
- Evans WJ, Campbell WW. Sarcopenia and age-related changes in body composition and functional capacity. 1993;123:465–468. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner RN, et al. Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. 1998;147:755–763. - PubMed
-
- Roubenoff R. Sarcopenia: A major modifiable cause of frailty in the elderly: Sarcopenia in aging. 2000;4:140–142. - PubMed
-
- Janssen I, Shepard DS, Katzmarzyk PT, Roubenoff R. The healthcare costs of sarcopenia in the United States. 2004;52:80–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

