Surface-modified solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery of docetaxel: enhanced intestinal absorption and lymphatic uptake
- PMID: 24531717
- PMCID: PMC3894956
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S56648
Surface-modified solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery of docetaxel: enhanced intestinal absorption and lymphatic uptake
Abstract
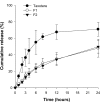
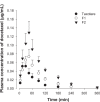
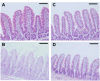
Docetaxel is a potent anticancer drug, but development of an oral formulation has been hindered mainly due to its poor oral bioavailability. In this study, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) surface-modified by Tween 80 or D-alpha-tocopheryl poly(ethylene glycol 1000) succinate (TPGS 1000) were prepared and evaluated in terms of their feasibility as oral delivery systems for docetaxel. Tween 80-emulsified and TPGS 1000-emulsified tristearin-based lipidic nanoparticles were prepared by a solvent-diffusion method, and their particle size distribution, zeta potential, drug loading, and particle morphology were characterized. An in vitro release study showed a sustained-release profile of docetaxel from the SLNs compared with an intravenous docetaxel formulation (Taxotere®). Tween 80-emulsified SLNs showed enhanced intestinal absorption, lymphatic uptake, and relative oral bioavailability of docetaxel compared with Taxotere in rats. These results may be attributable to the absorption-enhancing effects of the tristearin nanoparticle. Moreover, compared with Tween 80-emulsified SLNs, the intestinal absorption and relative oral bioavailability of docetaxel in rats were further improved in TPGS 1000-emulsified SLNs, probably due to better inhibition of drug efflux by TPGS 1000, along with intestinal lymphatic uptake. Taken together, it is worth noting that these surface-modified SLNs may serve as efficient oral delivery systems for docetaxel.
Keywords: bioavailability; docetaxel; lymphatic uptake; solid lipid nanoparticles; toxicity; vitamin E TPGS.
Figures



References
-
- van Waterschoot RA, Lagas JS, Wagenaar E, et al. Absence of both cytochrome P450 3A and P-glycoprotein dramatically increases docetaxel oral bioavailability and risk of intestinal toxicity. Cancer Res. 2009;69(23):8996–9002. - PubMed
-
- Clarke SJ, Rivory LP. Clinical pharmacokinetics of docetaxel. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999;36(2):99–114. - PubMed
-
- Yoon I, Han S, Choi YH, et al. Saturable sinusoidal uptake is rate-determining process in hepatic elimination of docetaxel in rats. Xenobiotica. 2012;42(11):1110–1119. - PubMed
-
- Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Cremophor EL. the drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(13):1590–1598. - PubMed
-
- Peltier S, Oger JM, Lagarce F, Couet W, Benoit JP. Enhanced oral paclitaxel bioavailability after administration of paclitaxel-loaded lipid nanocapsules. Pharm Res. 2006;23(6):1243–1250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

