Altered fecal microbiota composition associated with food allergy in infants
- PMID: 24532064
- PMCID: PMC3993190
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00003-14
Altered fecal microbiota composition associated with food allergy in infants
Abstract
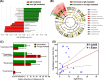
Increasing evidence suggests that perturbations in the intestinal microbiota composition of infants are implicated in the pathogenesis of food allergy (FA), while the actual structure and composition of the intestinal microbiota in human beings with FA remain unclear. Microbial diversity and composition were analyzed with parallel barcoded 454 pyrosequencing targeting the 16S rRNA gene hypervariable V1-V3 regions in the feces of 34 infants with FA (17 IgE mediated and 17 non-IgE mediated) and 45 healthy controls. Here, we showed that several key FA-associated bacterial phylotypes, but not the overall microbiota diversity, significantly changed in infancy fecal microbiota with FA and were associated with the development of FA. The proportion of abundant Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria phyla were significantly reduced, while the Firmicutes phylum was highly enriched in the FA group (P < 0.05). Abundant Clostridiaceae 1 organisms were prevalent in infants with FA at the family level (P = 0.016). FA-enriched phylotypes negatively correlated with interleukin-10, for example, the genera Enterococcus and Staphylococcus. Despite profound interindividual variability, levels of 20 predominant genera were significantly different between the FA and healthy control groups (P < 0.05). Infants with IgE-mediated FA had increased levels of Clostridium sensu stricto and Anaerobacter and decreased levels of Bacteroides and Clostridium XVIII (P < 0.05). A positive correlation was observed between Clostridium sensu stricto and serum-specific IgE (R = 0.655, P < 0.001). The specific microbiota signature could distinguish infants with IgE-mediated FA from non-IgE-mediated ones. Detailed microbiota analysis of a well-characterized cohort of infants with FA showed that dysbiosis of fecal microbiota with several FA-associated key phylotypes may play a pathogenic role in FA.
Figures

References
-
- Noti M, Wojno ED, Kim BS, Siracusa MC, Giacomin PR, Nair MG, Benitez AJ, Ruymann KR, Muir AB, Hill DA, Chikwava KR, Moghaddam AE, Sattentau QJ, Alex A, Zhou C, Yearley JH, Menard-Katcher P, Kubo M, Obata-Ninomiya K, Karasuyama H, Comeau MR, Brown-Whitehorn T, de Waal Malefyt R, Sleiman PM, Hakonarson H, Cianferoni A, Falk GW, Wang ML, Spergel JM, Artis D. 2013. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-elicited basophil responses promote eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat. Med. 19:1005–1013. 10.1038/nm.3281 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang M, Karlsson C, Olsson C, Adlerberth I, Wold AE, Strachan DP, Martricardi PM, Aberg N, Perkin MR, Tripodi S, Coates AR, Hesselmar B, Saalman R, Molin G, Ahrne S. 2008. Reduced diversity in the early fecal microbiota of infants with atopic eczema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 121:129–134. 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.09.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Noval Rivas M, Burton OT, Wise P, Zhang YQ, Hobson SA, Garcia Lloret M, Chehoud C, Kuczynski J, DeSantis T, Warrington J, Hyde ER, Petrosino JF, Gerber GK, Bry L, Oettgen HC, Mazmanian SK, Chatila TA. 2013. A microbiota signature associated with experimental food allergy promotes allergic sensitization and anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 131:201–212. 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.10.026 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

