Cerecidins, novel lantibiotics from Bacillus cereus with potent antimicrobial activity
- PMID: 24532070
- PMCID: PMC3993178
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03751-13
Cerecidins, novel lantibiotics from Bacillus cereus with potent antimicrobial activity
Abstract
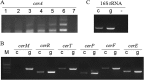
Lantibiotics are ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified antimicrobial peptides that are widely produced by Gram-positive bacteria, including many species of the Bacillus group. In the present study, one novel gene cluster coding lantibiotic cerecidins was unveiled in Bacillus cereus strain As 1.1846 through genomic mining and PCR screening. The designated cer locus is different from that of conventional class II lantibiotics in that it included seven tandem precursor cerA genes, one modification gene (cerM), two processing genes (cerT and cerP), one orphan regulator gene (cerR), and two immunity genes (cerF and cerE). In addition, one unprecedented quorum sensing component, comQXPA, was inserted between cerM and cerR. The expression of cerecidins was not detected in this strain of B. cereus, which might be due to repressed transcription of cerM. We constitutively coexpressed cerA genes and cerM in Escherichia coli, and purified precerecidins were proteolytically processed with the endoproteinase GluC and a truncated version of putative serine protease CerP. Thus, two natural variants of cerecidins A1 and A7 were obtained which contained two terminal nonoverlapping thioether rings rarely found in lantibiotics. Both cerecidins A1 and A7 were active against a broad spectrum of Gram-positive bacteria. Cerecidin A7, especially its mutant Dhb13A, showed remarkable efficacy against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MDRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE), and even Streptomyces.
Figures

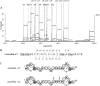
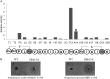
Similar articles
-
CerR, a Single-Domain Regulatory Protein of the LuxR Family, Promotes Cerecidin Production and Immunity in Bacillus cereus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Feb 14;84(5):e02245-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02245-17. Print 2018 Mar 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29247062 Free PMC article.
-
The Bacillus cereus group is an excellent reservoir of novel lanthipeptides.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Mar;81(5):1765-74. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03758-14. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25548056 Free PMC article.
-
Production of the novel two-peptide lantibiotic lichenicidin by Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 26;4(8):e6788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006788. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19707558 Free PMC article.
-
Class I and Class II Lanthipeptides Produced by Bacillus spp.J Nat Prod. 2015 Nov 25;78(11):2850-66. doi: 10.1021/np500424y. Epub 2015 Oct 8. J Nat Prod. 2015. PMID: 26448102 Review.
-
Epidermin and gallidermin: Staphylococcal lantibiotics.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Jan;304(1):63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.08.012. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24119540 Review.
Cited by
-
The Characterization, Biological Activities, and Potential Applications of the Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Bacillus spp.: A Comprehensive Review.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jun;17(3):1624-1647. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10447-5. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39739161 Review.
-
Bibacillin 1: a two-component lantibiotic from Bacillus thuringiensis.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 Sep 4;5(10):1060-73. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00192c. Online ahead of print. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39268544 Free PMC article.
-
Four Novel Leaderless Bacteriocins, Bacin A1, A2, A3, and A4 Exhibit Potent Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0094522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00945-22. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36000904 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of the class II lanthipeptide protease LicP for sequence-specific, traceless peptide bond cleavage.Chem Sci. 2015 Nov 1;6(11):6270-6279. doi: 10.1039/c5sc02329g. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 30090246 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics and Their Bioproducts: A Promising Approach for Targeting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 25;11(10):2393. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11102393. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37894051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnison PG, Bibb MJ, Bierbaum G, Bowers AA, Bugni TS, Bulaj G, Camarero JA, Campopiano DJ, Challis GL, Clardy J, Cotter PD, Craik DJ, Dawson M, Dittmann E, Donadio S, Dorrestein PC, Entian KD, Fischbach MA, Garavelli JS, Goransson U, Gruber CW, Haft DH, Hemscheidt TK, Hertweck C, Hill C, Horswill AR, Jaspars M, Kelly WL, Klinman JP, Kuipers OP, Link AJ, Liu W, Marahiel MA, Mitchell DA, Moll GN, Moore BS, Muller R, Nair SK, Nes IF, Norris GE, Olivera BM, Onaka H, Patchett ML, Piel J, Reaney MJ, Rebuffat S, Ross RP, Sahl HG, Schmidt EW, Selsted ME, Severinov K, Shen B, Sivonen K, Smith L, Stein T, Sussmuth RD, Tagg JR, Tang GL, Truman AW, Vederas JC, Walsh CT, Walton JD, Wenzel SC, Willey JM, van der Donk WA. 2013. Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Nat. Prod. Rep. 30:108–160. 10.1039/c2np20085f - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

