Impact of social determinants of health on outcomes for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review
- PMID: 24532079
- PMCID: PMC7029167
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-014-0195-0
Impact of social determinants of health on outcomes for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review
Abstract
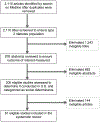
Social determinants of health include the social and economic conditions that influence health status. Research into the impact of social determinants on individuals with type 2 diabetes has largely focused on the prevention of or risk of developing diabetes. No review exists summarizing the impact of social determinants of health outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. This systematic review examined whether social determinants of health have an impact on health outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Medline was searched for articles that (a) were published in English (b) targeted adults, ages 18 + years, (c) had a study population which was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, (d) the study was done in the United States, and (e) the study measured at least one of the outcome measures-glycemic control, cholesterol (LDL), blood pressure, quality of life or cost. Using a reproducible strategy, 2,110 articles were identified, and 61 were reviewed based on inclusion criteria. Twelve were categorized as Economic Stability and Education, 17 were categorized as Social and Community Context, 28 were categorized as Health and Health Care, and three were categorized as Neighborhood and Built Environment. Based on the studies reviewed, social determinants have an impact on glycemic control, LDL, and blood pressure to varying degrees. The impact on cost and quality of life was not often measured, but when quality of life was investigated, it did show significance. More research is needed to better characterize the direct impact of social determinants of health on health outcomes in diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Marmot M Social determinants of health inequities. The Lancet 2005; 365:1099–1104. - PubMed
-
- Healthy People. Secretary’s Advisory Committee on Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Objectives for 2020. Healthy People 2020: An Opportunity to Address the Societal Determinants of Health in the United States. July 26, 2010. Available from: http://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topicsobjectives2020/overview.aspx?top...
-
- Bonnefoy J, Morgan A, Kelly MP, Butt J, Bergman V. Constructing the evidence base on the social determinants of health: a guide. Geneva, Switzerland: The Measurement and Evidence Knowledge Network (MEKM) of the WHO commission on Social Determinants of Health, 2007.
-
- Marmot M, Wilkinson R, eds. Social Determinants of Health. Second edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical