Advantages of proteins being disordered
- PMID: 24532081
- PMCID: PMC4005706
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2443
Advantages of proteins being disordered
Abstract
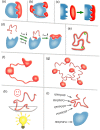
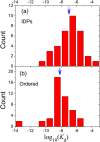
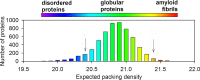
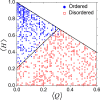
The past decade has witnessed great advances in our understanding of protein structure-function relationships in terms of the ubiquitous existence of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) and intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs). The structural disorder of IDPs/IDRs enables them to play essential functions that are complementary to those of ordered proteins. In addition, IDPs/IDRs are persistent in evolution. Therefore, they are expected to possess some advantages over ordered proteins. In this review, we summarize and survey nine possible advantages of IDPs/IDRs: economizing genome/protein resources, overcoming steric restrictions in binding, achieving high specificity with low affinity, increasing binding rate, facilitating posttranslational modifications, enabling flexible linkers, preventing aggregation, providing resistance to non-native conditions, and allowing compatibility with more available sequences. Some potential advantages of IDPs/IDRs are not well understood and require both experimental and theoretical approaches to decipher. The connection with protein design is also briefly discussed.
Keywords: drug design; flexibility; intrinsically disordered proteins; molecular recognition; protein design; protein function; protein-protein interaction.
© 2014 The Protein Society.
Figures
References
-
- Tompa P. Intrinsically disordered proteins: a 10-year recap. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012;37:509–516. - PubMed
-
- Huang YQ, Liu ZR. Intrinsically disordered proteins: the new sequence-structure-function relations. Acta Phys Chim Sin. 2010;26:2061–2072.
-
- Dunker AK, Lawson JD, Brown CJ, Williams RM, Romero P, Oh JS, Oldfield CJ, Campen AM, Ratliff CR, Hipps KW, Ausio J, Nissen MS, Reeves R, Kang C, Kissinger CR, Bailey RW, Griswold MD, Chiu W, Garner EC, Obradovic Z. Intrinsically disordered protein. J Mol Graph Model. 2001;19:26–59. - PubMed
-
- Wright PE, Dyson HJ. Intrinsically unstructured proteins: re-assessing the protein structure-function paradigm. J Mol Biol. 1999;293:321–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

