Protein methylation and interaction with the antiproliferative gene, BTG2/TIS21/Pc3
- PMID: 24532495
- PMCID: PMC3936616
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.2.292
Protein methylation and interaction with the antiproliferative gene, BTG2/TIS21/Pc3
Abstract
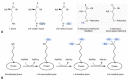
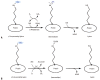
The last one and half a decade witnessed an outstanding re-emergence of attention and remarkable progress in the field of protein methylation. In the present article, we describe the early discoveries in research and review the role protein methylation played in the biological function of the antiproliferative gene, BTG2/TIS21/PC3.
Keywords: APRO (antiproliferative) genes; BTG2 (B-cell translocation gene 2); PKMT; PRMT; Protein methylation; TIS21 (TPA-inducible sequences 21); protein methyltransferases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kim S, Paik WK. Studies on the origin of epsilon-N-methyl-L-lysine in protein. J Biol Chem. 1965;240:4629–4634. - PubMed
-
- Schoenheimer R, Ratner S, Rittenberg D. Studies on protein metabolism: VII. The metabolism of tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1939;127:333–344.
-
- Ambler RP, Rees MW. Epsilon-N-methyl-lysine in bacterial flagellar protein. Nature. 1959;184:56–57. - PubMed
-
- Murray K. The occurence of epsilon-N-methyl lysine in histones. Biochemistry. 1964;3:10–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

