Proteomic analysis of cap-dependent translation identifies LARP1 as a key regulator of 5'TOP mRNA translation
- PMID: 24532714
- PMCID: PMC3937514
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.231407.113
Proteomic analysis of cap-dependent translation identifies LARP1 as a key regulator of 5'TOP mRNA translation
Abstract
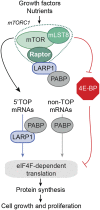
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) promotes cell growth and proliferation by promoting mRNA translation and increasing the protein synthetic capacity of the cell. Although mTOR globally promotes translation by regulating the mRNA 5' cap-binding protein eIF4E (eukaryotic initiation factor 4E), it also preferentially regulates the translation of certain classes of mRNA via unclear mechanisms. To help fill this gap in knowledge, we performed a quantitative proteomic screen to identify proteins that associate with the mRNA 5' cap in an mTOR-dependent manner. Using this approach, we identified many potential regulatory factors, including the putative RNA-binding protein LARP1 (La-related protein 1). Our results indicate that LARP1 associates with actively translating ribosomes via PABP and that LARP1 stimulates the translation of mRNAs containing a 5' terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) motif, encoding for components of the translational machinery. We found that LARP1 associates with the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and is required for global protein synthesis as well as cell growth and proliferation. Together, these data reveal important molecular mechanisms involved in TOP mRNA translation and implicate LARP1 as an important regulator of cell growth and proliferation.
Keywords: 5′TOP; LARP1; mRNA; mTOR; proteomics; translation.
Figures


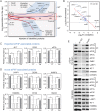
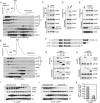
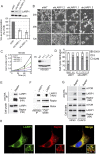
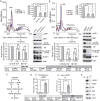
References
-
- Alain T, Morita M, Fonseca BD, Yanagiya A, Siddiqui N, Bhat M, Zammit D, Marcus V, Metrakos P, Voyer LA, et al. 2012. eIF4E/4E-BP ratio predicts the efficacy of mTOR targeted therapies. Cancer Res 72: 6468–6476 - PubMed
-
- Aoki K, Adachi S, Homoto M, Kusano H, Koike K, Natsume T 2013. LARP1 specifically recognizes the 3′ terminus of poly(A) mRNA. FEBS Lett 587: 2173–2178 - PubMed
-
- Blagden SP, Gatt MK, Archambault V, Lada K, Ichihara K, Lilley KS, Inoue YH, Glover DM 2009. Drosophila Larp associates with poly(A)-binding protein and is required for male fertility and syncytial embryo development. Dev Biol 334: 186–197 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
