Workforce Disengagement Stressors and Retiree Alcohol Misuse: The Mediating Effects of Sleep Problems and the Moderating Effects of Gender
- PMID: 24532849
- PMCID: PMC3922824
- DOI: 10.1177/0018726711435250
Workforce Disengagement Stressors and Retiree Alcohol Misuse: The Mediating Effects of Sleep Problems and the Moderating Effects of Gender
Abstract
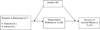
We generate and test a moderated mediation model of the effects of two retirement-related stressors (namely, financial and marital) on the severity of alcohol misuse among retirees. We posit that in addition to using alcohol to cope with stressors in retirement, alcohol may also be used to self-medicate the secondary, sleep-related effects of such stressors, and that gender serves as a key boundary condition, moderating the impact of such stressors on sleep-related problems, and of sleep-related problems on alcohol misuse. Using longitudinal data collected from a sample of 292 retirees, our findings generally support this model, suggesting that both stressors are associated with the severity of alcohol misuse among male retirees. Moreover, our findings demonstrate that -- for male retirees -- the effect of both stressors on the severity of alcohol misuse is to a large extent secondary to the stressors themselves, mediated by the sleep-related problems they may generate.
Keywords: alcohol misuse; retirement; sleep-related problems; stressors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A cohort study on self-reported role stressors at work and poor sleep: does sense of coherence moderate or mediate the associations?Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2018 May;91(4):445-456. doi: 10.1007/s00420-018-1294-7. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2018. PMID: 29383438
-
Aging and drinking problems among mature adults: the moderating effects of positive alcohol expectancies and workforce disengagement.J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2008 Jan;69(1):151-9. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2008.69.151. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18080075
-
Work stressors, sleep quality, and alcohol-related problems across deployment: A parallel process latent growth modeling approach among Navy members.Stress Health. 2017 Oct;33(4):339-347. doi: 10.1002/smi.2712. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Stress Health. 2017. PMID: 27723222
-
An Economic Perspective on Personality Traits and Alcohol Misuse: Evidence from the Health and Retirement Study.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2015 Jun;18(2):75-92. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2015. PMID: 26230999
-
Gambling Problems Are Associated with Alcohol Misuse and Insomnia: Results from a Representative National Telephone Survey.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 22;18(13):6683. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18136683. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34206276 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The lingering effects of work context: Ambient work-unit characteristics and the impact of retirement on alcohol consumption.Hum Relat. 2019 Apr;72(4):675-705. doi: 10.1177/0018726718772883. Epub 2018 May 30. Hum Relat. 2019. PMID: 30905973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams DB, Wilson GT. Effects of alcohol on social anxiety in women: Cognitive versus physiological arousal. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 1979;88:161–173. - PubMed
-
- Aiken LS, West SG. Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications; 1991.
-
- Åkerstedt T, Knutsson A, Westerholm P, Theorell T, Alfredsson L, Kecklund G. Sleep disturbances, work stress and work hours: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2002;53(3):741–748. - PubMed
-
- Allison PD. Change scores as dependent variables in regression analysis. Sociological Methodology. 1990;20:93–114.
-
- Ancoli-Israel S, Roth T. Characteristics of insomnia in the United States: Results of the 1991 national sleep foundation survey. I. Sleep. 1999;22(Suppl 2):S347–S353. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources