Single-step Radiosyntheses of '18F-Labeled Click Synthons' from Azide-functionalized Diaryliodonium Salts
- PMID: 24532989
- PMCID: PMC3922306
- DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201200695
Single-step Radiosyntheses of '18F-Labeled Click Synthons' from Azide-functionalized Diaryliodonium Salts
Abstract
Positron emission tomography (PET) is an increasingly important biomedical imaging technique that relies on the development of radiotracers labeled with positron-emitters to achieve biochemical specificity. Fluorine-18 (t1/2 = 109.7 min) is an attractive positron-emitting radiolabel for organic radiotracers, primarily because of its longer half-life and greater availability relative to those for the main alternative, carbon-11 (t1/2 = 20.4 min). Rapid simple methods are sought for labeling prospective PET radiotracers with fluorine-18 from cyclotron-produced aqueous [18F]fluoride ion, which must often be converted first into a suitably reactive labeling synthon for use in a subsequent labelling reaction. Use of 18F-labeled synthons in 'click chemistry' attracts increasing attention for labeling PE Tradiotracers. Here we describe rapid single-step radiosyntheses of azido- or azidomethyl-bearing [18F]fluoroarenes from the reactions of diaryliodonium salts with no-carrier-added [18F]fluoride ion within a microfluidic apparatus to provide previously poorly accessible 18F-labeled click synthons in radiochemical yields of 15% for [18F]4-fluorophenyl azide and about 40% for each of the [18F](azidomethyl)-fluorobenzenes. The radiosyntheses of the latter synthons was possible under 'wet conditions', so obviating the need to dry the cyclotron-produced [18F]fluoride ion and greatly enhancing the practicality of the method.
Keywords: Click chemistry; Hypervalent compounds; Imaging agents; Isotopic labeling; Radiochemistry.
Figures

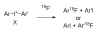


References
-
- Cai L, Lu S, Pike VW. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008;178:2853–2873.
-
- Ruth TJ, Wolf AP. Radiochim. Acta. 1979;26:21–24.
- Guillaume M, Luxen A, Nebeling B, Argentini M, Clark JC, Pike VW. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1991;42:749–762.
- Qaim SM, Clark JC, Crouzel C, Guillaume M, Helmeke HJ, Nebeling B, Pike VW, Stöcklin G. In: Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography. Stöcklin G, Pike VW, editors. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht, Netherlands: 1993. pp. 1–43.
-
- Huisgen R. In: 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Chemistry. Padwa A, editor. Wiley; New York: 1984.
- Kolb HC, Finn MG, Sharpless KB. Angew. Chem. 2001;113:2056–2075. - PubMed
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001;40:2004–2021. - PubMed
- Kolb HC, Sharpless KB. Drug Discovery Today. 2003;8:1128–1137. - PubMed
- Mamidyala SK, Finn MG. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010;39:1252–1261. - PubMed
-
- Miller PM, Long NJ, Vilar R, Gee AD. Angew. Chem. 2008;120:9136–9172. - PubMed
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008;47:8998–9033. - PubMed
- Glaser M, Robbins EG, Label J. Compds. Radiopharm. 2009;52:407–414.
- Mamat C, Ramenda T, Wuest FR. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2009;6:21–34.
- Wängler C, Schirrmacher R, Bartenstein P, Wängler B. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010;17:1092–1116. - PubMed
- Nwe K, Brechbiel MW. Cancer Biotherapy Radiopharmaceut. 2009;24:289–302. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Glaser M, Arstadt E. Bioconj. Chem. 2007;18:989–993. - PubMed
- Sirion U, Kim HJ, Lee JH, Seo JW, Lee BS, Lee SJ, Oh SJ, Chi DY. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007;48:3953–3957.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
