A descriptive study on compliance of spectacle-wear in children of primary schools at Qassim Province, Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 24533022
- PMCID: PMC3921058
- DOI: 10.12816/0006057
A descriptive study on compliance of spectacle-wear in children of primary schools at Qassim Province, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: Uncorrected Refractive errors are the most common cause of avoidable visual impairment in children worldwide. Importance of school screening of refractive errors are one of the most important initiatives outlined in WHO Vision 2020 targets for control of avoidable visual impairment in children. But the benefit depends on the compliance of the spectacle wear by children.
Purpose: To study the prevalence and determinants of compliance of spectacle wear among children and to investigate the reasons of non compliance associated with the spectacle wear in primary school children.
Materials and methods: This was a cross-sectional descriptive study of 631 students who had been prescribed spectacles for constant wear during school screening programme done by our Department of Optometry, College of Applied Medical Sciences, Qassim University during 2010-2011. After six months, experienced Optometrists conducted a follow-up visit where these students were assessed about spectacle compliance. Information on age, gender, type of refractive error, reasons for non compliance were collected and analyzed.
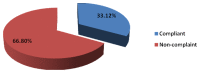
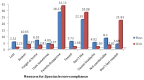
Results: The non-compliance rate of spectacle wear in primary school children is 66.80%. A significantly higher proportion of boys 244(69.13%) were not wearing their spectacles compared to girls 178 (64.03%) (P<0.05). Non-compliance was not related to age of the students (P<0.05), but older and myopic children were slightly more non-compliant. The main reasons for non-compliance in primary school boys and girls for using spectacles were disapproving spectacle wear by parents, not like to wear spectacles, broken spectacles and many children feel spectacles are not needed or causes head ache.
Conclusions: Comprehensive eye care for primary school children with refractive error is practised in Qassim Province, but limited information is available on the magnitude of the compliance for spectacle wear and their reasons. School children were not compliant because of many issues that could and should be addressed. This information is crucial for establishing a program and will strengthen its efforts for a better eye care in primary school children with refractive errors.
Keywords: Primary School children; Qassim; Saudi Arabia; Spectacle Compliance.
Figures
References
-
- Castanon Holguin AM, Congdon N, Patel N, Ratcliffe A, Esteso P, Toledo Flores S, Gilbert D, Pereyra Rito MA, Munoz B. Factors associated with spectacle-wear compliance in school-aged Mexican children. Invest Ophthalmol and Vis Sci. 2006;47(3):925–8. - PubMed
-
- Congdon NG, Patel N, Esteso P, Chikwembani F, Webber F, Msithini RB, Ratcliffe A. The association between refractive cutoffs for spectacle provision and visual improvement among school-aged children in South Africa. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008;92:13–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources