Parasite neuropeptide biology: Seeding rational drug target selection?
- PMID: 24533265
- PMCID: PMC3862435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2011.10.004
Parasite neuropeptide biology: Seeding rational drug target selection?
Abstract
The rationale for identifying drug targets within helminth neuromuscular signalling systems is based on the premise that adequate nerve and muscle function is essential for many of the key behavioural determinants of helminth parasitism, including sensory perception/host location, invasion, locomotion/orientation, attachment, feeding and reproduction. This premise is validated by the tendency of current anthelmintics to act on classical neurotransmitter-gated ion channels present on helminth nerve and/or muscle, yielding therapeutic endpoints associated with paralysis and/or death. Supplementary to classical neurotransmitters, helminth nervous systems are peptide-rich and encompass associated biosynthetic and signal transduction components - putative drug targets that remain to be exploited by anthelmintic chemotherapy. At this time, no neuropeptide system-targeting lead compounds have been reported, and given that our basic knowledge of neuropeptide biology in parasitic helminths remains inadequate, the short-term prospects for such drugs remain poor. Here, we review current knowledge of neuropeptide signalling in Nematoda and Platyhelminthes, and highlight a suite of 19 protein families that yield deleterious phenotypes in helminth reverse genetics screens. We suggest that orthologues of some of these peptidergic signalling components represent appealing therapeutic targets in parasitic helminths.
Keywords: Anthelmintic; Nervous system; Neuromuscular; Receptor; Signalling.
Figures
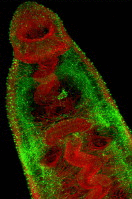
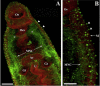
References
-
- Abad P., Gouzy J., Aury J.M., Castagnone-Sereno P., Danchin E.G., Deleury E., Perfus-Barbeoch L., Anthouard V., Artiguenave F., Blok V.C., Caillaud M.C., Coutinho P.M., Dasilva C., De Luca F., Deau F., Esquibet M., Flutre T., Goldstone J.V., Hamamouch N., Hewezi T., Jaillon O., Jubin C., Leonetti P., Magliano M., Maier T.R., Markov G.V., McVeigh P., Pesole G., Poulain J., Robinson-Rechavi M., Sallet E., Ségurens B., Steinbach D., Tytgat T., Ugarte E., van Ghelder C., Veronico P., Baum T.J., Blaxter M., Bleve-Zacheo T., Davis E.L., Ewbank J.J., Favery B., Grenier E., Henrissat B., Jones J.T., Laudet V., Maule A.G., Quesneville H., Rosso M.N., Schiex T., Smant G., Weissenbach J., Wincker P. Genome sequence of the metazoan plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:909–915. - PubMed
-
- Ahier A., Khayath N., Vicogne J., Dissous C. Insulin receptors and glucose uptake in the human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Parasite. 2008;15:573–579. - PubMed
-
- Arena J.P., Liu K.K., Paress P.S., Schaeffer J.M., Cully D.F. Expression of a glutamate-activated chloride current in Xenopus oocytes injected with Caenorhabditis elegans RNA: evidence for modulation by avermectin. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1992;15:339–348. - PubMed
-
- Asada A., Orii H., Watanabe K., Tsubaki M. Planarian peptidylglycine-hydroxylating monooxygenase, a neuropeptide processing enzyme, colocalizes with cytochrome b561 along the central nervous system. FEBS J. 2005;272:942–955. - PubMed
-
- Atchison W.D., Geary T.G., Manning B., VandeWaa E.A., Thompson D.P. Comparative neuromuscular blocking actions of levamisole and pyrantel-type anthelmintics on rat and gastrointestinal nematode somatic muscle. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1992;112:133–143. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

