Methodological challenges in utilizing miRNAs as circulating biomarkers
- PMID: 24533657
- PMCID: PMC3943687
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12236
Methodological challenges in utilizing miRNAs as circulating biomarkers
Abstract
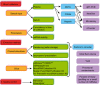
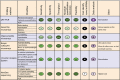
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important regulators in the post-transcriptional control of gene expression. The discovery of their presence not only in tissues but also in extratissular fluids, including blood, urine and cerebro-spinal fluid, together with their changes in expression in various pathological conditions, has implicated these extracellular miRNAs as informative biomarkers of disease. However, exploiting miRNAs in this capacity requires methodological rigour. Here, we report several key procedural aspects of miRNA isolation from plasma and serum, as exemplified by research in cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases. We also highlight the advantages and disadvantages of various profiling methods to determine the expression levels of plasma- and serum-derived miRNAs. Attention to such methodological details is critical, as circulating miRNAs become diagnostic tools for various human diseases.
Keywords: biomarkers; circulating microRNAs; microRNA; plasma; profiling; real-time PCR; serum.
© 2014 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Amiel J, Pontual de L, Henrion-Caude A. miRNA, development and disease. Adv Genet. 2012;80:1–36. - PubMed
-
- Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O'Connell RM, et al. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:839–45. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki HI, Miyazono K. Emerging complexity of microRNA generation cascades. J Biochem. 2011;149:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Thum T, Galuppo P, Wolf C, et al. MicroRNAs in the human heart: a clue to fetal gene reprogramming in heart failure. Circulation. 2007;116:258–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

