Practical aspects of NMR signal assignment in larger and challenging proteins
- PMID: 24534088
- PMCID: PMC3951217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2013.12.001
Practical aspects of NMR signal assignment in larger and challenging proteins
Abstract
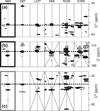
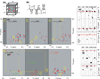
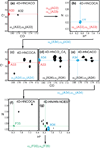
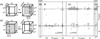
NMR has matured into a technique routinely employed for studying proteins in near physiological conditions. However, applications to larger proteins are impeded by the complexity of the various correlation maps necessary to assign NMR signals. This article reviews the data analysis techniques traditionally employed for resonance assignment and describes alternative protocols necessary for overcoming challenges in large protein spectra. In particular, simultaneous analysis of multiple spectra may help overcome ambiguities or may reveal correlations in an indirect manner. Similarly, visualization of orthogonal planes in a multidimensional spectrum can provide alternative assignment procedures. We describe examples of such strategies for assignment of backbone, methyl, and nOe resonances. We describe experimental aspects of data acquisition for the related experiments and provide guidelines for preliminary studies. Focus is placed on large folded monomeric proteins and examples are provided for 37, 48, 53, and 81 kDa proteins.
Keywords: Large protein; Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR); Resonance assignment; Spectra analysis; Spectral overlap.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures










References
-
- Keller RLJ. The Computer Aided Resonance Assignment Tutorial, Cantina Verlag, Goldau. 2004
-
- Vranken WF, Boucher W, Stevens TJ, Fogh RH, Pajon A, Llinas M, Ulrich EL, Markley JL, Ionides J, Laue ED. The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005;59:687–696. - PubMed
-
- Goddard T, Kneller D. SPARKY 3. San Fransisco: Univeristy of California;
-
- Johnson BA, Blevins RA. NMR view: a computer program for the visualization and analysis of NMR data. J. Biomol. NMR. 1994;4:603–614. - PubMed
-
- Peti W, Page R. Strategies to maximize heterologous protein expression in Escherichia coli with minimal cost. Protein Exp. Purif. 2007;51:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

