A genome-wide association meta-analysis of plasma Aβ peptides concentrations in the elderly
- PMID: 24535457
- PMCID: PMC4418478
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2013.185
A genome-wide association meta-analysis of plasma Aβ peptides concentrations in the elderly
Abstract
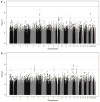
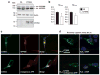
Amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides are the major components of senile plaques, one of the main pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer disease (AD). However, Aβ peptides' functions are not fully understood and seem to be highly pleiotropic. We hypothesized that plasma Aβ peptides concentrations could be a suitable endophenotype for a genome-wide association study (GWAS) designed to (i) identify novel genetic factors involved in amyloid precursor protein metabolism and (ii) highlight relevant Aβ-related physiological and pathophysiological processes. Hence, we performed a genome-wide association meta-analysis of four studies totaling 3 528 healthy individuals of European descent and for whom plasma Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 peptides levels had been quantified. Although we did not observe any genome-wide significant locus, we identified 18 suggestive loci (P<1 × 10(-)(5)). Enrichment-pathway analyses revealed canonical pathways mainly involved in neuronal functions, for example, axonal guidance signaling. We also assessed the biological impact of the gene most strongly associated with plasma Aβ1-42 levels (cortexin 3, CTXN3) on APP metabolism in vitro and found that the gene protein was able to modulate Aβ1-42 secretion. In conclusion, our study results suggest that plasma Aβ peptides levels are valid endophenotypes in GWASs and can be used to characterize the metabolism and functions of APP and its metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De Strooper B, Annaert W. Proteolytic processing and cell biological functions of the amyloid precursor protein. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 11):1857–1870. - PubMed
-
- Yazawa H, Yu ZX, Takeda, Le Y, Gong W, Ferrans VJ, et al. Beta amyloid peptide (Abeta42) is internalized via the G-protein-coupled receptor FPRL1 and forms fibrillar aggregates in macrophages. FASEB J. 2001;15:2454–2462. - PubMed
-
- Maezawa I, Jin L-W, Woltjer RL, Maeda N, Martin GM, Montine TJ, Montine KS. Apolipoprotein E isoforms and apolipoprotein AI protect from amyloid precursor protein carboxy terminal fragment-associated cytotoxicity. J Neurochem. 2004;91:1312–1321. - PubMed
-
- Yankner BA, Duffy LK, Kirschner DA. Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science. 1990;250:279–282. - PubMed
-
- Thomas T, Thomas G, McLendon C, Sutton T, Mullan M. Beta-amyloid-mediated vasoactivity and vascular endothelial damage. Nature. 1996;380:168–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 AG030514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037212/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG034550/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG007232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

