Resveratrol decreases fructose-induced oxidative stress, mediated by NADPH oxidase via an AMPK-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 24547812
- PMCID: PMC4243851
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12648
Resveratrol decreases fructose-induced oxidative stress, mediated by NADPH oxidase via an AMPK-dependent mechanism
Abstract
Background and purpose: Oxidative stress is an important pathogenic factor in the development of hypertension. Resveratrol, the main antioxidant in red wine, improves NO bioavailability and prevents cardiovascular disease. The aim of this study was to examine whether resveratrol decreases the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby reducing BP in rats with fructose-induced hypertension.
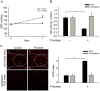
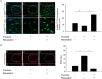
Experimental approach: Rats were fed 10% fructose with or without resveratrol (10 mg·kg(-1) ·day(-1) ) for 1 week or for 4 weeks with resveratrol treatment beginning at week 2; systolic BP (SBP) was measured by tail-cuff method. Endogenous in vivo O2 (-) production in the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) was determined with dihydroethidium. Real-time PCR and immunoblotting analyses were used to quantify RNA and protein expression levels.
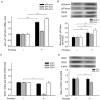
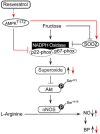
Key results: In fructose-fed rats, ROS levels in the NTS were higher, whereas the NO level was significantly decreased. Also, RNA and protein levels of NADPH oxidase subunits (p67, p22-phox) were elevated, superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) reduced and AMP-activated PK (AMPK) T172 phosphorylation levels in the NTS were lower in fructose-fed rats. Treatment with the AMPK activator resveratrol decreased levels of NADPH oxidase subunits and ROS, and increased NO and SOD2 levels in the NTS of fructose-fed rats. Administration of resveratrol, in combination with fructose at week 0 and later at week 2, significantly reduced the SBP of fructose-fed rats.
Conclusions and implications: Collectively, resveratrol decreased BP through the phosphorylation of AMPK, Akt and neuronal NOS in fructose-fed rats. These novel findings suggest that resveratrol may be a potential pharmacological candidate for the treatment of hypertension.
Keywords: AMPK; hypertension; nitrogen oxides; nucleus tractus solitarii; resveratrol.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Resveratrol regulates blood pressure by enhancing AMPK signaling to downregulate a Rac1-derived NADPH oxidase in the central nervous system.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Jul 1;125(1):40-48. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00686.2017. Epub 2018 Mar 1. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 29494287
-
Antihypertensive Potential of Coenzyme Q10 via Free Radical Scavenging and Enhanced Akt-nNOS Signaling in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarii in Rats.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019 Mar;63(6):e1801042. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201801042. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019. PMID: 30668894
-
Resveratrol Inhibition of Rac1-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species by AMPK Decreases Blood Pressure in a Fructose-Induced Rat Model of Hypertension.Sci Rep. 2016 May 3;6:25342. doi: 10.1038/srep25342. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27138844 Free PMC article.
-
Cross talk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Oct 1;51(7):1289-301. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.06.033. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21777669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of reactive oxygen species in brainstem in neural mechanisms of hypertension.Auton Neurosci. 2008 Nov 3;142(1-2):20-4. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2008.06.001. Epub 2008 Jul 22. Auton Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18650132 Review.
Cited by
-
Delphinidin attenuates pathological cardiac hypertrophy via the AMPK/NOX/MAPK signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Mar 25;12(6):5362-5383. doi: 10.18632/aging.102956. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32209725 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of resveratrol and 5-azacytydine improves osteogenesis of metabolic syndrome mesenchymal stem cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Oct;22(10):4771-4793. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13731. Epub 2018 Jul 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29999247 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical modulators of mitochondria: the search for chemopreventive agents and supportive therapeutics.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2014 Sep 4;7(9):913-42. doi: 10.3390/ph7090913. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25192192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Release of Nitric Oxide Is Involved in the β-Arrestin1-Induced Antihypertensive Effect in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 18;12:694135. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.694135. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34220554 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the molecular and clinical aspects of resveratrol in Alzheimer's disease: a review.3 Biotech. 2025 Sep;15(9):284. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04451-x. Epub 2025 Aug 6. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40777747 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baur JA, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:493–506. - PubMed
-
- Bavithra S, Selvakumar K, Krishnamoorthy G, Venkataraman P, Arunakaran J. Melatonin attenuates polychlorinated biphenyls induced apoptosis in the neuronal cells of cerebral cortex and cerebellum of adult male rats – in vivo. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2013;36:152–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

