Zerumbone-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway in a human lymphoblastic leukemia cell line
- PMID: 24549090
- PMCID: PMC3897324
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S54346
Zerumbone-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway in a human lymphoblastic leukemia cell line
Abstract
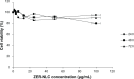
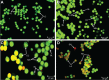
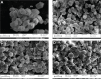
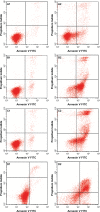
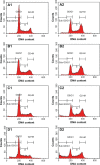
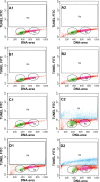
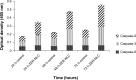
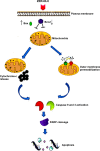
This investigation evaluated the antileukemia properties of a zerumbone (ZER)-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) prepared by hot high-pressure homogenization techniques in an acute human lymphoblastic leukemia (Jurkat) cell line in vitro. The apoptogenic effect of the ZER-NLC on Jurkat cells was determined by fluorescent and electron microscopy, Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate, Tdt-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling assay, cell cycle analysis, and caspase activity. An MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5 diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay showed that ZER-NLC did not have adverse effects on normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. ZER-NLC arrested the Jurkat cells at G2/M phase with inactivation of cyclin B1 protein. The study also showed that the antiproliferative effect of ZER-NLC on Jurkat cells is through the intrinsic apoptotic pathway via activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9, release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria into the cytosol, and subsequent cleavage of poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase (PARP). These findings show that the ZER-NLC is a potentially useful treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in humans.
Keywords: apoptosis; cell cycle arrest; mitochondrial pathway; zerumbone-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier.
Figures


References
-
- Al Haj NA, Abdullah R, Ibrahim S, Bustamam A. Tamoxifen drug loading solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by hot high pressure homogenization techniques. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;3:219–224.
-
- How CW, Abdullah R, Abbasalipourkabir R. Physicochemical properties of nanostructured lipid carriers as colloidal carrier system stabilized with polysorbate 20 and polysorbate 80. Afr J Biotechnol. 2011;10:1684–1689.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

