Nanodrug delivery systems: a promising technology for detection, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer
- PMID: 24550101
- PMCID: PMC4037475
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-014-0089-8
Nanodrug delivery systems: a promising technology for detection, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer
Abstract
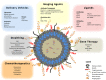
Nanotechnology has enabled the development of novel therapeutic and diagnostic strategies, such as advances in targeted drug delivery systems, versatile molecular imaging modalities, stimulus responsive components for fabrication, and potential theranostic agents in cancer therapy. Nanoparticle modifications such as conjugation with polyethylene glycol have been used to increase the duration of nanoparticles in blood circulation and reduce renal clearance rates. Such modifications to nanoparticle fabrication are the initial steps toward clinical translation of nanoparticles. Additionally, the development of targeted drug delivery systems has substantially contributed to the therapeutic efficacy of anti-cancer drugs and cancer gene therapies compared with nontargeted conventional delivery systems. Although multifunctional nanoparticles offer numerous advantages, their complex nature imparts challenges in reproducibility and concerns of toxicity. A thorough understanding of the biological behavior of nanoparticle systems is strongly warranted prior to testing such systems in a clinical setting. Translation of novel nanodrug delivery systems from the bench to the bedside will require a collective approach. The present review focuses on recent research efforts citing relevant examples of advanced nanodrug delivery and imaging systems developed for cancer therapy. Additionally, this review highlights the newest technologies such as microfluidics and biomimetics that can aid in the development and speedy translation of nanodrug delivery systems to the clinic.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

