Cell competition: how to eliminate your neighbours
- PMID: 24550108
- PMCID: PMC3929405
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.079129
Cell competition: how to eliminate your neighbours
Abstract
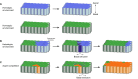
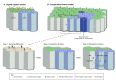
A conventional view of development is that cells cooperate to build an organism. However, based on studies of Drosophila, it has been known for years that viable cells can be eliminated by their neighbours through a process termed cell competition. New studies in mammals have revealed that this process is universal and that many factors and mechanisms are conserved. During cell competition, cells with lower translation rates or those with lower levels of proteins involved in signal transduction, polarity and cellular growth can survive in a homogenous environment but are killed when surrounded by cells of higher fitness. Here, we discuss recent advances in the field as well as the mechanistic steps involved in this phenomenon, which have shed light on how and why cell competition exists in developing and adult organisms.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Losers; Minute; Myc; Super-competition; Winners.
Figures
References
-
- Abrams J. M. (2002). Competition and compensation: coupled to death in development and cancer. Cell 110, 403–406 - PubMed
-
- Abrams J. M., White K., Fessler L. I., Steller H. (1993). Programmed cell death during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development 117, 29–43 - PubMed
-
- Agrawal N., Kango M., Mishra A., Sinha P. (1995). Neoplastic transformation and aberrant cell-cell interactions in genetic mosaics of lethal(2)giant larvae (lgl), a tumor suppressor gene of Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 172, 218–229 - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros-Arias L., Saavedra V., Morata G. (2013). Cell competition may function either as tumour-suppressing or as tumour-stimulating factor in Drosophila. Oncogene (in press). doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.407 - PubMed
-
- Bergmann A., Agapite J., McCall K., Steller H. (1998). The Drosophila gene hid is a direct molecular target of Ras-dependent survival signaling. Cell 95, 331–341 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

