Efficacy and safety of ascending methotrexate dose in combination with adalimumab: the randomised CONCERTO trial
- PMID: 24550168
- PMCID: PMC4431334
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204769
Efficacy and safety of ascending methotrexate dose in combination with adalimumab: the randomised CONCERTO trial
Abstract
Objective: CONCERTO was a randomised, double-blind, parallel-armed study of methotrexate (MTX) in combination with adalimumab to assess whether an increasing trend of efficacy and decreased safety exists when increasing MTX dose in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
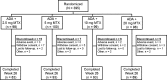
Methods: Early, biologic and MTX-naive RA patients (N=395) were evenly randomised to open-label adalimumab (40 mg every other week) plus weekly blinded 2.5, 5, 10 or 20 mg MTX for 26 weeks. Clinical, radiographic and functional outcomes were analysed using two-sided linear trend tests or one-way analysis of covariance.
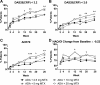
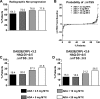
Results: Statistically significant increasing trends were observed in the proportion of patients achieving the primary endpoint, 28-joint count disease activity score with C reactive protein (DAS28(CRP)) <3.2 (42.9%, 44.0%, 56.6% and 60.2% for 2.5, 5, 10 or 20 mg/week MTX, respectively), DAS28(CRP) <2.6 and American College of Rheumatology 50/70/90 responses with increasing doses of MTX in combination with adalimumab. No statistical differences in minimal clinically important differences in physical function were detected. Statistically significant trends for achieving low disease activity and remission were demonstrated with increasing MTX dose by validated clinical indices; differences comparing 10 and 20 mg MTX were minimal. Adalimumab serum concentrations increased with ascending dose up to 10 mg MTX. More patients experienced infectious adverse events with increasing MTX dose.
Conclusions: Increasing doses of MTX in combination with adalimumab demonstrated a statistically significant trend in improved clinical outcomes that mimicked the adalimumab pharmacokinetic profile. In early RA patients initiating adalimumab combination therapy, efficacy of 10 and 20 mg/week MTX appeared equivalent.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures

References
-
- Weinblatt ME. Efficacy of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 1995;34(Suppl 2):43–8. - PubMed
-
- Swierkot J, Szechinski J. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Rep 2006;58:473–92. - PubMed
-
- Cutolo M, Bisso A, Sulli A, et al. Antiproliferative and antiinflammatory effects of methotrexate on cultured differentiating myeloid monocytic cells (THP-1) but not on synovial macrophages from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2000;27:2551–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

