Cartilage-specific deletion of Mig-6 results in osteoarthritis-like disorder with excessive articular chondrocyte proliferation
- PMID: 24550287
- PMCID: PMC3932925
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1400744111
Cartilage-specific deletion of Mig-6 results in osteoarthritis-like disorder with excessive articular chondrocyte proliferation
Abstract
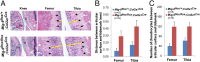
A deficiency of mitogen-inducible gene-6 (Mig-6) in mice leads to the development of an early-onset, osteoarthritis (OA)-like disorder in multiple synovial joints, underlying its importance in maintaining joint homeostasis. Here we determined what joint tissues Mig-6 is expressed in and what role chondrocytes play in the Mig-6-deficient OA-like disorder. A Mig-6/lacZ reporter mouse strain expressing β-galactosidase under the control of the Mig-6 gene promoter was generated to determine Mig-6 expression in joint tissues. By β-galactosidase staining, we demonstrated that Mig-6 was uniquely expressed in the cells across the entire surface of the synovial joint cavity, including chondrocytes in the superficial zone of articular cartilage and in the meniscus, as well as synovial lining cells. By crossing Mig-6-floxed mice to Col2a1-Cre transgenic mice, to generate cartilage-specific deletion of Mig-6, we demonstrated that deficiency of Mig-6 in the chondrocytes results in a joint phenotype that only partially recapitulates the OA-like disorder of the Mig-6-deficient mice: Ubiquitous deletion of Mig-6 led to the OA-like disorder in multiple joints, whereas cartilage-specific deletion affected the knees but rarely other joints. Furthermore, chondrocytes with Mig-6 deficiency showed excessive proliferative activities along with enhanced EGF receptor signaling in the articular cartilage and in the abnormally formed osteophytes. Our findings provide insight into the crucial requirement for Mig-6 in maintaining joint homeostasis and in regulating chondrocyte activities in the synovial joints. Our data also suggest that other cell types are required for fully developing the Mig-6-deficient OA-like disorder.
Keywords: EGFR; Errfi1; Gene 33; RALT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Zhang YW, Vande Woude GF. Mig-6, signal transduction, stress response and cancer. Cell Cycle. 2007;6(5):507–513. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YW, Vande Woude GF. MIG-6 and SPRY2 in the regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: Balancing act via negative feedback loops. In: Cheng Y, editor. Future Aspects of Tumor Suppressor Gene. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech; 2013. pp. 199–221.
-
- Anastasi S, et al. Feedback inhibition by RALT controls signal output by the ErbB network. Oncogene. 2003;22(27):4221–4234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

