Ischemic neurons recruit natural killer cells that accelerate brain infarction
- PMID: 24550298
- PMCID: PMC3932858
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1315943111
Ischemic neurons recruit natural killer cells that accelerate brain infarction
Abstract
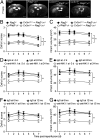
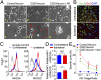
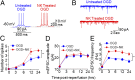
Brain ischemia and reperfusion activate the immune system. The abrupt development of brain ischemic lesions suggests that innate immune cells may shape the outcome of stroke. Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphocytes that can be swiftly mobilized during the earliest phases of immune responses, but their role during stroke remains unknown. Herein, we found that NK cells infiltrated the ischemic lesions of the human brain. In a mouse model of cerebral ischemia, ischemic neuron-derived fractalkine recruited NK cells, which subsequently determined the size of brain lesions in a T and B cell-independent manner. NK cell-mediated exacerbation of brain infarction occurred rapidly after ischemia via the disruption of NK cell tolerance, augmenting local inflammation and neuronal hyperactivity. Therefore, NK cells catalyzed neuronal death in the ischemic brain.
Keywords: innate immunity; ischemic stroke; middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kleinschnitz C, et al. Early detrimental T-cell effects in experimental cerebral ischemia are neither related to adaptive immunity nor thrombus formation. Blood. 2010;115(18):3835–3842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

