Trichomonas vaginalis metronidazole resistance is associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms in the nitroreductase genes ntr4Tv and ntr6Tv
- PMID: 24550324
- PMCID: PMC3993245
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02370-13
Trichomonas vaginalis metronidazole resistance is associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms in the nitroreductase genes ntr4Tv and ntr6Tv
Abstract
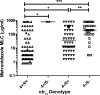
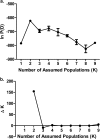
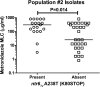
Metronidazole resistance in the sexually transmitted parasite Trichomonas vaginalis is a problematic public health issue. We have identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in two nitroreductase genes (ntr4Tv and ntr6Tv) associated with resistance. These SNPs were associated with one of two distinct T. vaginalis populations identified by multilocus sequence typing, yet one SNP (ntr6Tv A238T), which results in a premature stop codon, was associated with resistance independent of population structure and may be of diagnostic value.
Figures

References
-
- Kirkcaldy RD, Augostini P, Asbel LE, Bernstein KT, Kerani RP, Mettenbrink CJ, Pathela P, Schwebke JR, Secor WE, Workowski KA, Davis D, Braxton J, Weinstock HS. 2012. Trichomonas vaginalis antimicrobial drug resistance in 6 US cities, STD Surveillance Network, 2009–2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 18:939–943. 10.3201/eid1806.111590 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wright JM, Webb RI, O'Donoghue P, Upcroft P, Upcroft JA. 2010. Hydrogenosomes of laboratory-induced metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis lines are downsized while those from clinically metronidazole-resistant isolates are not. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 57:171–176. 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2009.00455.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

