High activity of Fosfomycin and Rifampin against methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus biofilm in vitro and in an experimental foreign-body infection model
- PMID: 24550327
- PMCID: PMC3993211
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02420-12
High activity of Fosfomycin and Rifampin against methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus biofilm in vitro and in an experimental foreign-body infection model
Abstract
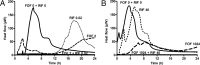
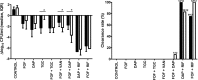
Increasing antimicrobial resistance reduces treatment options for implant-associated infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). We evaluated the activity of fosfomycin alone and in combination with vancomycin, daptomycin, rifampin, and tigecycline against MRSA (ATCC 43300) in a foreign-body (implantable cage) infection model. The MICs of the individual agents were as follows: fosfomycin, 1 μg/ml; daptomycin, 0.125 μg/ml; vancomycin, 1 μg/ml; rifampin, 0.04 μg/ml; and tigecycline, 0.125 μg/ml. Microcalorimetry showed synergistic activity of fosfomycin and rifampin at subinhibitory concentrations against planktonic and biofilm MRSA. In time-kill curves, fosfomycin exhibited time-dependent activity against MRSA with a reduction of 2.5 log10 CFU/ml at 128 × the MIC. In the animal model, planktonic bacteria in cage fluid were reduced by <1 log10 CFU/ml with fosfomycin and tigecycline, 1.7 log10 with daptomycin, 2.2 log10 with fosfomycin-tigecycline and fosfomycin-vancomycin, 3.8 log10 with fosfomycin-daptomycin, and >6.0 log10 with daptomycin-rifampin and fosfomycin-rifampin. Daptomycin-rifampin cured 67% of cage-associated infections and fosfomycin-rifampin cured 83%, whereas all single drugs (fosfomycin, daptomycin, and tigecycline) and rifampin-free fosfomycin combinations showed no cure of MRSA cage-associated infections. No emergence of fosfomycin resistance was observed in animals; however, a 4-fold increase in fosfomycin MIC (from 2 to 16 μg/ml) occurred in the fosfomycin-vancomycin group. In summary, the highest eradication of MRSA cage-associated infections was achieved with fosfomycin in combination with rifampin (83%). Fosfomycin may be used in combination with rifampin against MRSA implant-associated infections, but it cannot replace rifampin as an antibiofilm agent.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activities of fosfomycin and rifampin on planktonic and adherent Enterococcus faecalis strains in an experimental foreign-body infection model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(3):1284-93. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02583-12. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24145537 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of daptomycin in implant-associated infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: importance of combination with rifampin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Jul;53(7):2719-24. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00047-09. Epub 2009 Apr 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19364845 Free PMC article.
-
Fosfomycin-daptomycin and other fosfomycin combinations as alternative therapies in experimental foreign-body infection by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jan;57(1):606-10. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01570-12. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23089756 Free PMC article.
-
Use of daptomycin to treat infections with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates having vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentrations of 1.5 to 2 μg/mL.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Dec;47(12):1654-65. doi: 10.1177/1060028013508272. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259618 Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Probiotics and their Derivatives against Biofilm-Producing MRSA: A Scoping Review.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Dec 27;2022:4959487. doi: 10.1155/2022/4959487. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36605101 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rifamycins, Alone and in Combination.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016 Jul 1;6(7):a027011. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027011. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016. PMID: 27270559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Fosfomycin after Continuous Infusion Compared with Intermittent Infusion: a Randomized Crossover Study in Healthy Volunteers.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Dec 16;65(1):e01375-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01375-20. Print 2020 Dec 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 33106259 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Genomic Reveals Clonal Heterogeneity in Persistent Staphylococcus aureus Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 21;12:817841. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.817841. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35265532 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Scores and Machine Learning to Identify Patients With Acute Periprosthetic Joints Infections That Will Likely Fail Classical Irrigation and Debridement.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 May 3;8:550095. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.550095. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34012968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding Biofilms and Novel Approaches to the Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of Medical Device-Associated Infections.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2018 Dec;32(4):915-929. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2018.06.009. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2018. PMID: 30241715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

