Intracellular effects of the Hepatitis C virus nucleoside polymerase inhibitor RO5855 (Mericitabine Parent) and Ribavirin in combination
- PMID: 24550342
- PMCID: PMC3993208
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02250-13
Intracellular effects of the Hepatitis C virus nucleoside polymerase inhibitor RO5855 (Mericitabine Parent) and Ribavirin in combination
Abstract
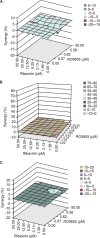
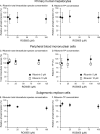
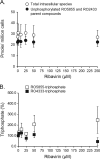
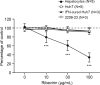
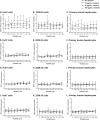
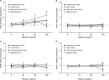
Mericitabine (RG7128) is the prodrug of a highly selective cytidine nucleoside analog inhibitor (RO5855) of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. This study evaluated the effects of combining RO5855 and ribavirin on HCV replication in the HCV subgenomic replicon by using two drug-drug interaction models. The effects of RO5855 and ribavirin on the intracellular metabolism of each compound, on interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression, and on the viability of hepatocyte-derived cells were also investigated. RO5855 and ribavirin had additive inhibitory activities against HCV subgenomic replicon replication in drug-drug interaction analyses. RO5855 did not affect the uptake or phosphorylation of ribavirin in primary human hepatocytes, human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, or genotype 1b (G1b) replicon cells. Similarly, ribavirin did not affect the concentrations of intracellular species derived from RO5855 in primary human hepatocytes or the formation of the triphosphorylated metabolites of RO5855. Ribavirin at concentrations of >40 μM significantly reduced the viability of primary hepatocytes but not of Huh7, the G1b replicon, or interferon-cured Huh7 cells. RO5855 alone or with ribavirin did not significantly alter the viability of Huh7 or G1b replicon cells, and it did not significantly affect the viability of primary hepatocytes when it was administered alone. The viability of primary hepatocytes was reduced when they were incubated with RO5855 and ribavirin, similar to the effects of ribavirin alone. RO5855 alone or with ribavirin had no effect on ISG mRNA levels in any of the cells tested. In conclusion, RO5855 did not show any unfavorable interactions with ribavirin in human hepatocytes or an HCV subgenomic replicon system.
Figures

References
-
- Bacon BR, Gordon SC, Lawitz E, Marcellin P, Vierling JM, Zeuzem S, Poordad F, Goodman ZD, Sings HL, Boparai N, Burroughs M, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Esteban R. 2011. Boceprevir for previously treated chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 364:1207–1217. 10.1056/NEJMoa1009482 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Flamm SL, Lawitz E, Jacobson I, Bourliere M, Hezode C, Vierling JM, Bacon BR, Niederau C, Sherman M, Goteti V, Sings HL, Barnard RO, Howe JA, Pedicone LD, Burroughs MH, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Poordad F. 2013. Boceprevir with peginterferon alfa-2a-ribavirin is effective for previously treated chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11:81–87. 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.10.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jacobson IM, McHutchison JG, Dusheiko G, Di Bisceglie AM, Reddy KR, Bzowej NH, Marcellin P, Muir AJ, Ferenci P, Flisiak R, George J, Rizzetto M, Shouval D, Sola R, Terg RA, Yoshida EM, Adda N, Bengtsson L, Sankoh AJ, Kieffer TL, George S, Kauffman RS, Zeuzem S. 2011. Telaprevir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 364:2405–2416. 10.1056/NEJMoa1012912 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Poordad F, McCone J, Jr, Bacon BR, Bruno S, Manns MP, Sulkowski MS, Jacobson IM, Reddy KR, Goodman ZD, Boparai N, DiNubile MJ, Sniukiene V, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Bronowicki JP. 2011. Boceprevir for untreated chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 364:1195–1206. 10.1056/NEJMoa1010494 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

