Molecular dynamics reveal BCR-ABL1 polymutants as a unique mechanism of resistance to PAN-BCR-ABL1 kinase inhibitor therapy
- PMID: 24550512
- PMCID: PMC3948238
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1321173111
Molecular dynamics reveal BCR-ABL1 polymutants as a unique mechanism of resistance to PAN-BCR-ABL1 kinase inhibitor therapy
Abstract
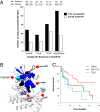
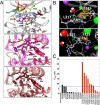
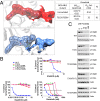
The acquisition of mutations within the BCR-ABL1 kinase domain is frequently associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) failure in chronic myeloid leukemia. Sensitive sequencing techniques have revealed a high prevalence of compound BCR-ABL1 mutations (polymutants) in patients failing TKI therapy. To investigate the molecular consequences of such complex mutant proteins with regards to TKI resistance, we determined by cloning techniques the presence of polymutants in a cohort of chronic-phase patients receiving imatinib followed by dasatinib therapy. The analysis revealed a high frequency of polymutant BCR-ABL1 alleles even after failure of frontline imatinib, and also the progressive exhaustion of the pool of unmutated BCR-ABL1 alleles over the course of sequential TKI therapy. Molecular dynamics analyses of the most frequent polymutants in complex with TKIs revealed the basis of TKI resistance. Modeling of BCR-ABL1 in complex with the potent pan-BCR-ABL1 TKI ponatinib highlighted potentially effective therapeutic strategies for patients carrying these recalcitrant and complex BCR-ABL1 mutant proteins while unveiling unique mechanisms of escape to ponatinib therapy.
Keywords: compound mutation; ponatinib resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.T. received grant support from Ariad, Novartis, and Bristol–Myers Squibb.
Figures
References
-
- Druker BJ, et al. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat Med. 1996;2(5):561–566. - PubMed
-
- Deininger M, et al. (2009) International randomized study of interferon vs STI571 (IRIS) 8-year follow up: Sustained survival and low risk for progression or events in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) treated with imatinib. Blood 114(22):1126 (abstr)
-
- Hochhaus A, La Rosée P. Imatinib therapy in chronic myelogenous leukemia: Strategies to avoid and overcome resistance. Leukemia. 2004;18(8):1321–1331. - PubMed
-
- Shah NP, et al. Multiple BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2002;2(2):117–125. - PubMed
-
- Löwenberg B. Minimal residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(15):1399–1401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

