Multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs regulate telomerase and TCF7, an important transcriptional regulator of the Wnt pathway
- PMID: 24551047
- PMCID: PMC3925088
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086990
Multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs regulate telomerase and TCF7, an important transcriptional regulator of the Wnt pathway
Abstract
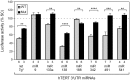
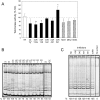
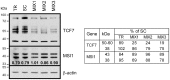
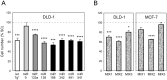
The human TERT (hTERT) gene encodes the telomerase catalytic subunit which plays a role in telomerase regulation. Telomerase is activated in more than 90% of all human malignancies and understanding how telomerase is regulated is necessary for implementation of successful anti-cancer therapies. microRNAs (miRNAs) are important regulators of gene expression in eukaryotic cells but evidence of their role in telomerase regulation has not been documented. To determine whether hTERT activity is regulated by multiple miRNAs, eight miRNAs which have putative binding sites in the hTERT 3'UTR together with miR-138-5p were evaluated in luciferase assays with a reporter containing the hTERT 3'UTR. Six miRNAs (let-7g*, miR-133a, miR-138-5p, miR-342-5p, miR-491-5p, and miR-541-3p) specifically inhibited the expression of the reporter luciferase-driven constructs and let-7g*, miR-133a, miR-138-5p, and miR-491-5p also downregulated endogenous telomerase activity in cells. Moreover, all six miRNAs significantly inhibited cell proliferation. miRNAs (miR-133a, miR-138-5p, 342-5p, 491-5p, 541-3p) also have predicted binding sites within the 3'UTR of three genes involved in Wnt signaling (TCF7, MSI1, and PAX5). These miRNAs inhibited the expression of the luciferase reporter constructs containing 3'UTRs of these genes and downregulated protein expression of the TCF7 transcription factor, which mediates the canonical Wnt pathway. Together, these results suggest the existence of a miRNA regulatory network involving the hTERT and Wnt pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
miR-1207-5p and miR-1266 suppress gastric cancer growth and invasion by targeting telomerase reverse transcriptase.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jan 30;5(1):e1034. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.553. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24481448 Free PMC article.
-
miR-512-5p suppresses tumor growth by targeting hTERT in telomerase positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 10;10(8):e0135265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135265. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26258591 Free PMC article.
-
miR-15a-5p suppresses endometrial cancer cell growth via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by inhibiting WNT3A.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Nov;21(21):4810-4818. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29164582
-
miR-140-5p and miR-140-3p: Key Actors in Aging-Related Diseases?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 28;23(19):11439. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911439. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-142-3p/5p role in cancer: From epigenetic regulation to immunomodulation.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Mar;42(2):e3931. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3931. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38379239 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-541-3p reverses cancer progression by directly targeting TGIF2 in non-small cell lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):12685-12695. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5241-5. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27448300
-
Profound changes in miRNA expression during cancer initiation by aflatoxin B1 and their abrogation by the chemopreventive triterpenoid CDDO-Im.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Nov;56(11):2382-2390. doi: 10.1002/mc.22635. Epub 2017 Sep 2. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28218475 Free PMC article.
-
TCF7 is suppressed by the androgen receptor via microRNA-1-mediated downregulation and is involved in the development of resistance to androgen deprivation in prostate cancer.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017 Jun;20(2):172-178. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2017.2. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017. PMID: 28220803
-
Physical Exercise and the Hallmarks of Breast Cancer: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;15(1):324. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010324. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36612320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular functions of RNA-binding protein, Musashi1, in stem and cancer cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 May 24;11(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01703-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32448364 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

