Same day identification and full panel antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles made possible by a combined lysis-filtration method with MALDI-TOF VITEK mass spectrometry and the VITEK2 system
- PMID: 24551067
- PMCID: PMC3925102
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087870
Same day identification and full panel antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles made possible by a combined lysis-filtration method with MALDI-TOF VITEK mass spectrometry and the VITEK2 system
Abstract
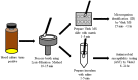
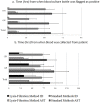
Rapid identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of microorganisms causing bloodstream infections or sepsis have the potential to improve patient care. This proof-of-principle study evaluates the Lysis-Filtration Method for identification as well as antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacteria directly from positive blood culture bottles in a clinical setting. A total of 100 non-duplicated positive blood cultures were tested and 1012 microorganism-antimicrobial combinations were assessed. An aliquot of non-charcoal blood culture broth was incubated with lysis buffer briefly before being filtered and washed. Microorganisms recovered from the filter membrane were first identified by using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight VITEK® Mass Spectrometry (VITEK MS). After quick identification from VITEK MS, filtered microorganisms were inoculated to VITEK®2 system for full panel antimicrobial susceptibility testing analysis. Of 100 bottles tested, the VITEK MS resulted in 94.0% correct organism identification to the species level. Compared to the conventional antimicrobial susceptibility testing methods, direct antimicrobial susceptibility testing from VITEK®2 resulted in 93.5% (946/1012) category agreement of antimicrobials tested, with 3.6% (36/1012) minor error, 1.7% (7/1012) major error, and 1.3% (13/1012) very major error of antimicrobials. The average time to identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing was 11.4 hours by using the Lysis-Filtration method for both VITEK MS and VITEK®2 compared to 56.3 hours by using conventional methods (p<0.00001). Thus, the same-day results of microorganism identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing directly from positive blood culture can be achieved and can be used for appropriate antibiotic therapy and antibiotic stewardship.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Romero-Gomez MP, Gomez-Gil R, Pano-Pardo JR, Mingorance J (2012) Identification and susceptibility testing of microorganism by direct inoculation from positive blood culture bottles by combining MALDI-TOF and Vitek-2 Compact is rapid and effective. J Infect 65: 513–20. - PubMed
-
- Wimmer JL, Long SW, Cernoch P, Land GA, Davis JR, et al. (2012) Strategy for rapid identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing of Gram-negative bacteria directly recovered from positive blood cultures using the Bruker MALDI Biotyper and the BD Phoenix system. J Clin Microbiol 50: 2452–4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schneiderhan W, Grundt A, Wörner S, Findeisen P, Neumaier M (2013) Workflow analysis of around-the-clock processing of blood culture samples and integrated MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analysis for the diagnosis of bloodstream infections. Clinical Chemistry doi:10.1373/clinchem.2012.198218. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang AM, Newton D, Kunapuli A, Gandhi TN, Washer LL, et al. (2013) Impact of Rapid Organism Identification via Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Combined With Antimicrobial Stewardship Team Intervention in Adult Patients With Bacteremia and Candidemia. Clin Infect Dis 57: 1237–1245. - PubMed
-
- Vlek AL, Bonten MJ, Boel CE (2012) Direct matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry improves appropriateness of antibiotic treatment of bacteremia. PloS ONE 7(3): e32589 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032589 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

