Microstructural parameters of bone evaluated using HR-pQCT correlate with the DXA-derived cortical index and the trabecular bone score in a cohort of randomly selected premenopausal women
- PMID: 24551194
- PMCID: PMC3923873
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088946
Microstructural parameters of bone evaluated using HR-pQCT correlate with the DXA-derived cortical index and the trabecular bone score in a cohort of randomly selected premenopausal women
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e98167
Abstract
Background: Areal bone mineral density is predictive for fracture risk. Microstructural bone parameters evaluated at the appendicular skeleton by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) display differences between healthy patients and fracture patients. With the simple geometry of the cortex at the distal tibial diaphysis, a cortical index of the tibia combining material and mechanical properties correlated highly with bone strength ex vivo. The trabecular bone score derived from the scan of the lumbar spine by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) correlated ex vivo with the micro architectural parameters. It is unknown if these microstructural correlations could be made in healthy premenopausal women.
Methods: Randomly selected women between 20-40 years of age were examined by DXA and HR-pQCT at the standard regions of interest and at customized sub regions to focus on cortical and trabecular parameters of strength separately. For cortical strength, at the distal tibia the volumetric cortical index was calculated directly from HR-pQCT and the areal cortical index was derived from the DXA scan using a Canny threshold-based tool. For trabecular strength, the trabecular bone score was calculated based on the DXA scan of the lumbar spine and was compared with the corresponding parameters derived from the HR-pQCT measurements at radius and tibia.
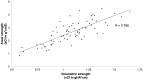
Results: Seventy-two healthy women were included (average age 33.8 years, average BMI 23.2 kg/m(2)). The areal cortical index correlated highly with the volumetric cortical index at the distal tibia (R = 0.798). The trabecular bone score correlated moderately with the microstructural parameters of the trabecular bone.
Conclusion: This study in randomly selected premenopausal women demonstrated that microstructural parameters of the bone evaluated by HR-pQCT correlated with the DXA derived parameters of skeletal regions containing predominantly cortical or cancellous bone. Whether these indexes are suitable for better predictions of the fracture risk deserves further investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Age-related reference data of bone microarchitecture, volumetric bone density, and bone strength parameters in a population of healthy Brazilian men: an HR-pQCT study.Osteoporos Int. 2022 Jun;33(6):1309-1321. doi: 10.1007/s00198-021-06288-5. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Osteoporos Int. 2022. PMID: 35059775
-
Bone density, geometry, microstructure, and stiffness: Relationships between peripheral and central skeletal sites assessed by DXA, HR-pQCT, and cQCT in premenopausal women.J Bone Miner Res. 2010 Oct;25(10):2229-38. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.111. J Bone Miner Res. 2010. PMID: 20499344 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of bone strength at the distal tibia by HR-pQCT and DXA.Bone. 2012 Jan;50(1):296-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.10.033. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Bone. 2012. PMID: 22088678
-
Best Performance Parameters of HR-pQCT to Predict Fragility Fracture: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Bone Miner Res. 2021 Dec;36(12):2381-2398. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4449. Epub 2021 Oct 18. J Bone Miner Res. 2021. PMID: 34585784 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography: research or clinical practice?Br J Radiol. 2023 Oct;96(1150):20221016. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20221016. Epub 2023 May 24. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37195008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological basis of bone strength: anatomy, physiology and measurement.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020 Sep 1;20(3):347-371. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020. PMID: 32877972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trabecular bone score and transilial bone trabecular histomorphometry in type 1 diabetes and healthy controls.Bone. 2020 Aug;137:115451. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115451. Epub 2020 May 22. Bone. 2020. PMID: 32450341 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of iliac crest tetracycline-labelled bone biopsy in osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease: An evaluation of 95 cases over a period of 25 years.Bone Rep. 2023 Sep 24;19:101715. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2023.101715. eCollection 2023 Dec. Bone Rep. 2023. PMID: 37811524 Free PMC article.
-
Normative data for peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT) bone parameters in Australian men.Bone Rep. 2021 Jul 8;15:101107. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2021.101107. eCollection 2021 Dec. Bone Rep. 2021. PMID: 34355046 Free PMC article.
-
Update on trabecular bone score.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Nov 11;66(5):694-706. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000559. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 36382759 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Study Group - no authors listed (1994) Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 843: 1–129. - PubMed
-
- Seeman E (2003) Invited Review: Pathogenesis of osteoporosis. J Appl Physiol 95: 2142–2151. - PubMed
-
- Seeman E, Delmas PD (2006) Bone quality—the material and structural basis of bone strength and fragility. N Engl J Med 354: 2250–2261. - PubMed
-
- Zebaze RM, Ghasem-Zadeh A, Bohte A, Iuliano-Burns S, Mirams M, et al. (2010) Intracortical remodelling and porosity in the distal radius and post-mortem femurs of women: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 375: 1729–1736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

