High-dose irradiation induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and developmental defects during Drosophila oogenesis
- PMID: 24551207
- PMCID: PMC3923870
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089009
High-dose irradiation induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and developmental defects during Drosophila oogenesis
Abstract
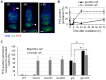
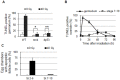
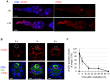
Ionizing radiation (IR) treatment induces a DNA damage response, including cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis in metazoan somatic cells. Because little has been reported in germline cells, we performed a temporal analysis of the DNA damage response utilizing Drosophila oogenesis as a model system. Oogenesis in the adult Drosophila female begins with the generation of 16-cell cyst by four mitotic divisions of a cystoblast derived from the germline stem cells. We found that high-dose irradiation induced S and G2 arrests in these mitotically dividing germline cells in a grp/Chk1- and mnk/Chk2-dependent manner. However, the upstream kinase mei-41, Drosophila ATR ortholog, was required for the S-phase checkpoint but not for the G2 arrest. As in somatic cells, mnk/Chk2 and dp53 were required for the major cell death observed in early oogenesis when oocyte selection and meiotic recombination occurs. Similar to the unscheduled DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) generated from defective repair during meiotic recombination, IR-induced DSBs produced developmental defects affecting the spherical morphology of meiotic chromosomes and dorsal-ventral patterning. Moreover, various morphological abnormalities in the ovary were detected after irradiation. Most of the IR-induced defects observed in oogenesis were reversible and were restored between 24 and 96 h after irradiation. These defects in oogenesis severely reduced daily egg production and the hatch rate of the embryos of irradiated female. In summary, irradiated germline cells induced DSBs, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and developmental defects resulting in reduction of egg production and defective embryogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Drosophila Claspin is required for the G2 arrest that is induced by DNA replication stress but not by DNA double-strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2012 Sep 1;11(9):741-52. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.06.007. Epub 2012 Jul 15. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012. PMID: 22796626
-
Activation of a meiotic checkpoint during Drosophila oogenesis regulates the translation of Gurken through Chk2/Mnk.Curr Biol. 2002 Oct 1;12(19):1645-51. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01165-x. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12361566
-
Cyclin G is involved in meiotic recombination repair in Drosophila melanogaster.J Cell Sci. 2012 Nov 15;125(Pt 22):5555-63. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113902. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22976300
-
Signaling between somatic follicle cells and the germline patterns the egg and embryo of Drosophila.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2020;140:55-86. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32591083 Review.
-
Asymmetric germ cell division and oocyte determination during Drosophila oogenesis.Int Rev Cytol. 2001;203:93-138. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(01)03005-4. Int Rev Cytol. 2001. PMID: 11131529 Review.
Cited by
-
Chk2-p53 and JNK in irradiation-induced cell death of hematopoietic progenitors and differentiated cells in Drosophila larval lymph gland.Biol Open. 2021 Aug 15;10(8):bio058809. doi: 10.1242/bio.058809. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Biol Open. 2021. PMID: 34328173 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation in P-element dysgenic sterility is associated with double-strand break repair and alternative splicing of TE transcripts.PLoS Genet. 2022 Dec 7;18(12):e1010080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010080. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36477699 Free PMC article.
-
Myc plays an important role in Drosophila P-M hybrid dysgenesis to eliminate germline cells with genetic damage.Commun Biol. 2020 Apr 22;3(1):185. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0923-3. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32322015 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and coordination of the different DNA damage responses in Drosophila.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 6;10:993257. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.993257. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36147740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of p53 isoforms in the DNA damage response during Drosophila oogenesis.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 7;9(1):11473. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47913-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31391501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song YH (2005) Drosophila melanogaster: a model for the study of DNA damage checkpoint response. Mol Cells 19: 167–179. - PubMed
-
- Drummond-Barbosa D, Spradling AC (2001) Stem cells and their progeny respond to nutritional changes during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev Biol 231: 265–278. - PubMed
-
- Abdu U, Brodsky M, Schupbach T (2002) Activation of a meiotic checkpoint during Drosophila oogenesis regulates the translation of Gurken through Chk2/Mnk. Curr Biol 12: 1645–1651. - PubMed
-
- Sibon OC, Laurencon A, Hawley R, Theurkauf WE (1999) The Drosophila ATM homologue Mei-41 has an essential checkpoint function at the midblastula transition. Curr Biol 9: 302–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

