Analysis of hepatitis B virus intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA and serum viral markers in treatment-naive patients with acute and chronic HBV infection
- PMID: 24551214
- PMCID: PMC3923869
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089046
Analysis of hepatitis B virus intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA and serum viral markers in treatment-naive patients with acute and chronic HBV infection
Erratum in
- PLoS One.2014 Apr;9(4):e96382. Yao, Weimin [corrected to Yao, Weiming]
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the relationships of intrahepatic cccDNA with serum HBsAg and with HBV DNA in treatment-naive patients throughout acute and chronic HBV infection.
Methods: A total of 120 patients who had a liver biopsy were enrolled, including 19 with acute hepatitis B (AHB), and 101 patients with chronic HBV infection (CHB) of whom were 10 in immune-tolerant (IT) phase, 59 in immune-clearance (IC) phase, 8 in low-replicative (LR) phase, and 24 in HBeAg-negative hepatitis (ENH) phase. Intrahepatic cccDNA, serum HBsAg and serum HBV DNA levels were comparatively analyzed.
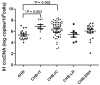
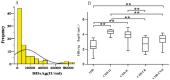
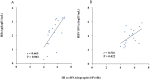
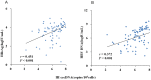
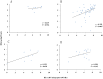
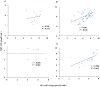
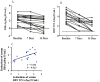
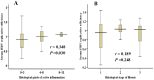
Results: The median intrahepatic cccDNA levels were 0.18 4.80, 3.81, 0.22 and 0.97 copies/cell for patients with AHB, CHB-IT, CHB-IC, CHB-LR, and CHB-ENH, respectively. In AHB patients, intrahepatic cccDNA was positively correlated with serum HBsAg (r = 0.665, P = 0.003), as well as serum HBV DNA (r = 0.536, P = 0.022). In CHB patients, intrahepatic cccDNA was positively correlated with serum HBsAg in the IC phase (r = 0.392, P = 0.005), and with serum HBV DNA in the IC phase (r = 0.301, P = 0.036) and ENH phase (r = 0.588, P = 0.013). HBV replicative efficiency, defined as the ratio of serum HBV DNA to intrahepatic cccDNA, was obviously lower in AHB and CHB-LR patients than in CHB-IT, CHB-IC and CHB-ENH patients (0.70 and 0.53 vs. 1.12, 1.09 and 0.99, P<0.001, values were logarithmic transformed for analysis). In CHB-IC patients, HBV replicative efficiency was positively correlated with histological activity index of liver inflammation (r = 0.308, P = 0.009).
Conclusion: Serum HBsAg and HBV DNA levels may reflect the amount of active intrahepatic cccDNA in treatment-naive AHB and CHB-IC patients. Reduced intrahepatic cccDNA and HBV replicative efficiency may imply effective immune control of HBV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases (2011) Chinese Medical Association, The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2010 version). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi (Chinese J Hepatol) 19: 13–24 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2011.01.007 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

