Computational studies on sirtuins from Trypanosoma cruzi: structures, conformations and interactions with phytochemicals
- PMID: 24551254
- PMCID: PMC3923677
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002689
Computational studies on sirtuins from Trypanosoma cruzi: structures, conformations and interactions with phytochemicals
Abstract
Background: The silent-information regulator 2 proteins, otherwise called sirtuins, are currently considered as emerging anti-parasitic targets. Nicotinamide, a pan-sirtuin inhibitor, is known to cause kinetoplast alterations and the arrested growth of T. cruzi, the protozoan responsible for Chagas disease. These observations suggested that sirtuins from this parasite (TcSir2rp1 and TcSir2rp3) could play an important role in the regulation of the parasitic cell cycle. Thus, their inhibition could be exploited for the development of novel anti-trypanosomal compounds.
Methods: Homology modeling was used to determine the three-dimensional features of the sirtuin TcSir2rp1 from T. cruzi. The apo-form of human SIRT2 and the same structure solved in complex with its co-substrate NAD(+) allowed the modeling of TcSir2rp1 in the open and closed conformational states. Molecular docking studies were then carried out. A library composed of fifty natural and diverse compounds that are known to be active against this parasite, was established based on the literature and virtually screened against TcSir2rp1 and TcSir2rp3, which was previously modeled by our group.
Results: In this study, two conformational states of TcSir2rp1 were described for the first time. The molecular docking results of compounds capable of binding sirtuins proved to be meaningful when the closed conformation of the protein was taken into account for calculations. This specific conformation was then used for the virtual screening of antritrypanosomal phytochemicals against TcSir2rp1 and TcSir2rp3. The calculations identified a limited number of scaffolds extracted from Vismia orientalis, Cussonia zimmermannii, Amomum aculeatum and Anacardium occidentale that potentially interact with both proteins.
Conclusions: The study provided reliable models for future structure-based drug design projects concerning sirtuins from T. cruzi. Molecular docking studies highlighted not only the advantages of performing in silico interaction studies on their closed conformations but they also suggested the potential mechanism of action of four phytochemicals known for their anti-trypanosomal activity in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


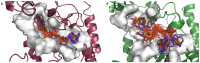
Similar articles
-
Chemical Constituents of Anacardium occidentale as Inhibitors of Trypanosoma cruzi Sirtuins.Molecules. 2019 Apr 3;24(7):1299. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071299. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30987092 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Inhibitors to Trypanosoma cruzi Sirtuins Based on Compounds Developed to Human Enzymes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 22;21(10):3659. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103659. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32455951 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of Trypanosoma cruzi Sir2 related protein 1 as potential drugs against Chagas disease.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Jan 22;12(1):e0006180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006180. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29357372 Free PMC article.
-
In silico tools to study molecular targets of neglected diseases: inhibition of TcSir2rp3, an epigenetic enzyme of Trypanosoma cruzi.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;122:203-229. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2020.04.001. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 32951812 Review.
-
Structural basis for sirtuin function: what we know and what we don't.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1804(8):1604-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.09.009. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19766737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual Screening in the Identification of Sirtuins' Activity Modulators.Molecules. 2022 Sep 1;27(17):5641. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175641. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Bichalcones as Sirtuin Inhibitors by Virtual Screening and In Vitro Testing.Molecules. 2018 Feb 14;23(2):416. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020416. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29443909 Free PMC article.
-
In silico structural characterization of protein targets for drug development against Trypanosoma cruzi.J Mol Model. 2016 Oct;22(10):244. doi: 10.1007/s00894-016-3115-9. Epub 2016 Sep 24. J Mol Model. 2016. PMID: 27665464
-
The Potential of Secondary Metabolites from Plants as Drugs or Leads against Protozoan Neglected Diseases-Part III: In-Silico Molecular Docking Investigations.Molecules. 2016 Oct 19;21(10):1389. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101389. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27775577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of DNA Methyltransferases From Natural Sources: A Computational Perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 10;9:1144. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01144. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30364171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hotez PJ, Bottazzi ME, Franco-Paredes C, Ault SK, Periago MR (2008) The Neglected Tropical Diseases of Latin America and the Caribbean: A Review of Disease Burden and Distribution and a Roadmap for Control and Elimination. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2 9: e300 doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000300 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Satoskar AR, Simon GL, Hotez PJ, Tsuji M (2009) Medical Parasitology. Austin, Texas: Landes Bioscience. 297p.
-
- Rassi A Jr, Rassi A, Marin JA (2010) Chagas disease. Lancet 375: 1388–1402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

