Rapid healing of cutaneous leishmaniasis by high-frequency electrocauterization and hydrogel wound care with or without DAC N-055: a randomized controlled phase IIa trial in Kabul
- PMID: 24551257
- PMCID: PMC3923720
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002694
Rapid healing of cutaneous leishmaniasis by high-frequency electrocauterization and hydrogel wound care with or without DAC N-055: a randomized controlled phase IIa trial in Kabul
Abstract
Background: Anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) due to Leishmania (L.) tropica infection is a chronic, frequently disfiguring skin disease with limited therapeutic options. In endemic countries healing of ulcerative lesions is often delayed by bacterial and/or fungal infections. Here, we studied a novel therapeutic concept to prevent superinfections, accelerate wound closure, and improve the cosmetic outcome of ACL.
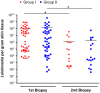
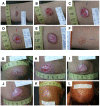
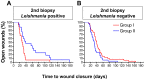
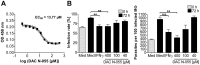
Methodology/principal findings: From 2004 to 2008 we performed a two-armed, randomized, double-blinded, phase IIa trial in Kabul, Afghanistan, with patients suffering from L. tropica CL. The skin lesions were treated with bipolar high-frequency electrocauterization (EC) followed by daily moist-wound-treatment (MWT) with polyacrylate hydrogel with (group I) or without (group II) pharmaceutical sodium chlorite (DAC N-055). Patients below age 5, with facial lesions, pregnancy, or serious comorbidities were excluded. The primary, photodocumented outcome was the time needed for complete lesion epithelialization. Biopsies for parasitological and (immuno)histopathological analyses were taken prior to EC (1(st)), after wound closure (2(nd)) and after 6 months (3(rd)). The mean duration for complete wound closure was short and indifferent in group I (59 patients, 43.1 d) and II (54 patients, 42 d; p = 0.83). In patients with Leishmania-positive 2(nd) biopsies DAC N-055 caused a more rapid wound epithelialization (37.2 d vs. 58.3 d; p = 0.08). Superinfections occurred in both groups at the same rate (8.8%). Except for one patient, reulcerations (10.2% in group I, 18.5% in group II; p = 0.158) were confined to cases with persistent high parasite loads after healing. In vitro, DAC N-055 showed a leishmanicidal effect on pro- and amastigotes.
Conclusions/significance: Compared to previous results with intralesional antimony injections, the EC plus MWT protocol led to more rapid wound closure. The tentatively lower rate of relapses and the acceleration of wound closure in a subgroup of patients with parasite persistence warrant future studies on the activity of DAC N-055.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00947362.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Bailey MS, Lockwood DN (2007) Cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Dermatol 25: 203–211. - PubMed
-
- Reithinger R, Dujardin JC, Louzir H, Pirmez C, Alexander B, et al. (2007) Cutaneous leishmaniasis. Lancet Infect Dis 7: 581–596. - PubMed
-
- WHO (2010) Control of Leishmaniasis. WHO Technical Report Series 949: 1–187.
-
- Bogdan C (2012) Leishmaniasis in Rheumatology, Hematology, and Oncology: Epidemiological, Immunological, and Clinical Aspects and Caveats. Ann Rheumatic Diseases 71 (suppl. 2) i60–i66. - PubMed
-
- Kibbi AG, Karam PG, Kurban AK (1987) Sporotrichoid leishmaniasis in patients from Saudi Arabia: clinical and histologic features. J Am Acad Dermatol 17: 759–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

