Overexpression of periostin is significantly correlated to the tumor angiogenesis and poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24551279
- PMCID: PMC3925903
Overexpression of periostin is significantly correlated to the tumor angiogenesis and poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
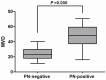
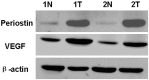
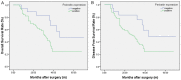
Recent studies have found that periostin (PN), as a kind of secreted glycoprotein, is closely related to the metastatic potential and prognosis of many kinds of tumors. This study aimed to examine the expression of PN in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and explore the relationship of PN expression with clinicopathologic factors, tumor angiogenesis and prognosis. The results showed that increased PN protein expression was prevalent in ESCC and was significantly associated with lymphatic metastasis (P=0.008), tumor differentiation (P=0.04), venous invasion (P=0.014) and TNM stage (P=0.001). Additionally, expression of PN was found to be an independent prognostic factor in ESCC patients. High expression of PN protein is closely correlated to the tumor progression and angiogenesis and poor survival of ESCC. Taken together, PN is a promising biomarker to identify individuals with poor prognostic potential and concludes the possibility of its use as a prognostic marker in patients with ESCC.
Keywords: Periostin; angiogenesis; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; prognosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of p53 expression with prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Sep 15;7(10):7158-63. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25400812 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced stratifin expression can serve as an independent prognostic factor for poor survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Dig Dis Sci. 2010 Sep;55(9):2552-60. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-1065-0. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20108042
-
Clinicopathology significance of podoplanin immunoreactivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Apr 15;7(5):2361-71. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24966946 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of microvessel density in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma-a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Nov;227:153644. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153644. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 34634564
-
Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in esophageal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.J BUON. 2013 Apr-Jun;18(2):398-406. J BUON. 2013. PMID: 23818352 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Periostin Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Periostin Silencing Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of Lung Cancer Cells via Regulation of MMP-2 Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 22;23(3):1240. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031240. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163164 Free PMC article.
-
Association between periostin and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jul;14(1):376-382. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6124. Epub 2017 May 5. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28693179 Free PMC article.
-
Periostin: A Matricellular Protein With Multiple Functions in Cancer Development and Progression.Front Oncol. 2018 Jun 12;8:225. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00225. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29946533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role and underlying mechanisms of the interstitial protein periostin in the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors.Oncol Lett. 2017 Nov;14(5):5099-5106. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6866. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29142596 Free PMC article.
-
The Blood Oxygenation T2* Values of Resectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas as Measured by 3T Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Association with Tumor Stage.Korean J Radiol. 2017 Jul-Aug;18(4):674-681. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2017.18.4.674. Epub 2017 May 19. Korean J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28670162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:2137–2150. - PubMed
-
- Sano A, Kato H, Sakurai S, Sakai M, Tanaka N, Inose T, Saito K, Sohda M, Nakajima M, Nakajima T, Kuwano H. CD24 expression is a novel prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:506–514. - PubMed
-
- Mariette C, Balon JM, Piessen G, Fabre S, Van Seuningen I, Triboulet JP. Pattern of recurrence following complete resection of esophageal carcinoma and factors predictive of recurrent disease. Cancer. 2003;97:1616–1623. - PubMed
-
- Ren Y, Cao B, Law S, Xie Y, Lee PY, Cheung L, Chen Y, Huang X, Chan HM, Zhao P, Luk J, Vande Woude G, Wong J. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes cancer cell migration and angiogenic factors expression: a prognostic marker of human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6190–6197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
