Temporal abstraction-based clinical phenotyping with Eureka!
- PMID: 24551400
- PMCID: PMC3900137
Temporal abstraction-based clinical phenotyping with Eureka!
Abstract
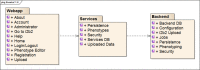
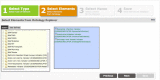
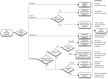
Temporal abstraction, a method for specifying and detecting temporal patterns in clinical databases, is very expressive and performs well, but it is difficult for clinical investigators and data analysts to understand. Such patterns are critical in phenotyping patients using their medical records in research and quality improvement. We have previously developed the Analytic Information Warehouse (AIW), which computes such phenotypes using temporal abstraction but requires software engineers to use. We have extended the AIW's web user interface, Eureka! Clinical Analytics, to support specifying phenotypes using an alternative model that we developed with clinical stakeholders. The software converts phenotypes from this model to that of temporal abstraction prior to data processing. The model can represent all phenotypes in a quality improvement project and a growing set of phenotypes in a multi-site research study. Phenotyping that is accessible to investigators and IT personnel may enable its broader adoption.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Medical temporal-knowledge discovery via temporal abstraction.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2009 Nov 14;2009:452-6. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2009. PMID: 20351898 Free PMC article.
-
The Analytic Information Warehouse (AIW): a platform for analytics using electronic health record data.J Biomed Inform. 2013 Jun;46(3):410-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2013.01.005. Epub 2013 Feb 9. J Biomed Inform. 2013. PMID: 23402960 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput phenotyping with temporal sequences.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021 Mar 18;28(4):772-781. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa288. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33313899 Free PMC article.
-
Review and evaluation of electronic health records-driven phenotype algorithm authoring tools for clinical and translational research.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2015 Nov;22(6):1251-60. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocv070. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2015. PMID: 26224336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical data mining and research in the allergy office.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Jun;10(3):171-7. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e328337bce6. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20179584 Review.
Cited by
-
Zero-shot interpretable phenotyping of postpartum hemorrhage using large language models.NPJ Digit Med. 2023 Nov 30;6(1):212. doi: 10.1038/s41746-023-00957-x. NPJ Digit Med. 2023. PMID: 38036723 Free PMC article.
-
A Method for EHR Phenotype Management in an i2b2 Data Warehouse.AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2019 May 6;2019:92-101. eCollection 2019. AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2019. PMID: 31258960 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an automated phenotyping algorithm for hepatorenal syndrome.J Biomed Inform. 2018 Apr;80:87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 9. J Biomed Inform. 2018. PMID: 29530803 Free PMC article.
-
I2b2-etl: Python application for importing electronic health data into the informatics for integrating biology and the bedside platform.Bioinformatics. 2022 Oct 14;38(20):4833-4836. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac595. Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36053173 Free PMC article.
-
A Modular Architecture for Electronic Health Record-Driven Phenotyping.AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2015 Mar 25;2015:147-51. eCollection 2015. AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2015. PMID: 26306258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blumenthal D. Implementation of the federal health information technology initiative. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(25):2426–31. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal D. Wiring the health system--origins and provisions of a new federal program. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(24):2323–9. - PubMed
-
- PheKB. Vanderbilt University; 2012. [cited 2013 Mar 13]; Available from: http://phekb.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
