Exploring the relationship between drug side-effects and therapeutic indications
- PMID: 24551427
- PMCID: PMC3900166
Exploring the relationship between drug side-effects and therapeutic indications
Abstract
Therapeutic indications and drug side-effects are both measureable human behavioral or physiological changes in response to the treatment. In modern drug development, both inferring potential therapeutic indications and identifying clinically important drug side-effects are challenging tasks. Previous studies have utilized either chemical structures or protein targets to predict indications and side-effects. In this study, we compared indication prediction using side-effect information and side-effect prediction using indication information against models using only chemical structures and protein targets. Experimental results based on 10-fold cross-validation, show that drug side-effects and therapeutic indications are the most predictive features for each other. In addition, we extracted 6,706 statistically highly correlated disease-side-effect pairs from all known drug-disease and drug-side-effect relationships. Many relationship pairs provide explicit repositioning hypotheses (e.g., drugs causing postural hypotension are potential candidates for hypertension) and clear adverse-reaction watch lists (e.g., drugs for heart failure possibly cause impotence). All data sets and highly correlated disease-side-effect relationships are available at http://astro.temple.edu/~tua87106/druganalysis.html.
Figures
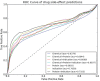
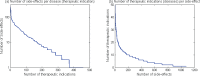
Similar articles
-
Exploring the associations between drug side-effects and therapeutic indications.J Biomed Inform. 2014 Oct;51:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2014.03.014. Epub 2014 Apr 13. J Biomed Inform. 2014. PMID: 24727480
-
Systematic drug repositioning based on clinical side-effects.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028025. Epub 2011 Dec 21. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22205936 Free PMC article.
-
Combining automatic table classification and relationship extraction in extracting anticancer drug-side effect pairs from full-text articles.J Biomed Inform. 2015 Feb;53:128-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Biomed Inform. 2015. PMID: 25445920 Free PMC article.
-
[Adverse Effect Predictions Based on Computational Toxicology Techniques and Large-scale Databases].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(2):185-190. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.17-00174-4. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 29386432 Review. Japanese.
-
Exploring DrugCentral: from molecular structures to clinical effects.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2023 Dec;37(12):681-694. doi: 10.1007/s10822-023-00529-x. Epub 2023 Sep 14. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2023. PMID: 37707619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unexpected beneficial effects of drugs: an analysis of cases in the Dutch spontaneous reporting system.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;77(10):1543-1551. doi: 10.1007/s00228-021-03142-9. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33884456
-
Machine Learning for Integrating Data in Biology and Medicine: Principles, Practice, and Opportunities.Inf Fusion. 2019 Oct;50:71-91. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Inf Fusion. 2019. PMID: 30467459 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring new relations between medical entities using literature curated term co-occurrences.JAMIA Open. 2019 Jul 1;2(3):378-385. doi: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooz022. eCollection 2019 Oct. JAMIA Open. 2019. PMID: 31984370 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative approaches for predicting in vivo effects of chemicals from their structural descriptors and the results of short-term biological assays.Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(11):1356-64. doi: 10.2174/1568026614666140506121116. Curr Top Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24805064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico methods for drug repurposing and pharmacology.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016 May;8(3):186-210. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1337. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27080087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
