Sample size estimation in epidemiologic studies
- PMID: 24551434
- PMCID: PMC3895825
Sample size estimation in epidemiologic studies
Abstract
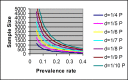
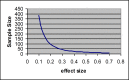
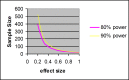
This review basically provided a conceptual framework for sample size calculation in epidemiologic studies with various designs and outcomes. The formula requirement of sample size was drawn based on statistical principles for both descriptive and comparative studies. The required sample size was estimated and presented graphically with different effect sizes and power of statistical test at 95% confidence level. This would help the clinicians to decide and ascertain a suitable sample size in research protocol in order to detect an effect of interest.
Keywords: Binary outcome; Comparative studies; Continuous outcome; Effect size; Sample size; Statistical power.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sample size estimation in diagnostic test studies of biomedical informatics.J Biomed Inform. 2014 Apr;48:193-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2014.02.013. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Biomed Inform. 2014. PMID: 24582925
-
The relationship between statistical power and predictor distribution in multilevel logistic regression: a simulation-based approach.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019 May 9;19(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12874-019-0742-8. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019. PMID: 31072299 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical power and sample size estimation for headache research: an overview and power calculation tools.Headache. 2005 May;45(5):414-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05092.x. Headache. 2005. PMID: 15953257 Review.
-
The detection of gene-environment interaction for continuous traits: should we deal with measurement error by bigger studies or better measurement?Int J Epidemiol. 2003 Feb;32(1):51-7. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyg002. Int J Epidemiol. 2003. PMID: 12690008
-
Subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials: quantifying the risks of false-positives and false-negatives.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(33):1-56. doi: 10.3310/hta5330. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701102 Review.
Cited by
-
Secondhand smoking exposure and quality of life among pregnant and postnatal women: a network approach.BMJ Open. 2022 Sep 16;12(9):e060635. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-060635. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36113943 Free PMC article.
-
Small-area methods for investigation of environment and health.Int J Epidemiol. 2020 Apr 1;49(2):686-699. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyaa006. Int J Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 32182344 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life among patients with esophageal, gastric, and colorectal cancer at Kenyatta National Hospital.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Mar;7(3):e2038. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2038. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38507287 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of short-term glycemic control and physical activity on health-related quality of life among type 2 diabetes receiving care in a tertiary health facility in Ogun State, Nigeria: a cross-sectional study.Pan Afr Med J. 2023 Jan 24;44:47. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2023.44.47.35680. eCollection 2023. Pan Afr Med J. 2023. PMID: 37070021 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Cipto Triage Method: A Single-Centre Study from Indonesia.Open Access Emerg Med. 2020 May 18;12:137-143. doi: 10.2147/OAEM.S246598. eCollection 2020. Open Access Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32547263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Houle TT, Penzien DB, Houle CK. Statistical power and sample size estimation for headache research: An overview and power calculation tools. Headache. 2005;45:414–8. - PubMed
-
- Fitzner K, Heckinger E. Sample size calculation and power analysis: a quick review. Diabetes Educ. 2010;36:701–7. - PubMed
-
- Detskey AS, Sackett DL. When was a negative clinical trial big enough? How many patients you needed depends on what you found. Arch Intern Med. 1985;145:709–12. - PubMed
-
- Livingston EH, Cassidy L. Statistical power and estimation of the number of required subjects for a study based on the t-test. J Surg Res. 2005;126:149–59. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
