Sample size estimation in epidemiologic studies
- PMID: 24551434
- PMCID: PMC3895825
Sample size estimation in epidemiologic studies
Abstract
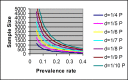
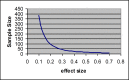
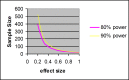
This review basically provided a conceptual framework for sample size calculation in epidemiologic studies with various designs and outcomes. The formula requirement of sample size was drawn based on statistical principles for both descriptive and comparative studies. The required sample size was estimated and presented graphically with different effect sizes and power of statistical test at 95% confidence level. This would help the clinicians to decide and ascertain a suitable sample size in research protocol in order to detect an effect of interest.
Keywords: Binary outcome; Comparative studies; Continuous outcome; Effect size; Sample size; Statistical power.
Figures
References
-
- Houle TT, Penzien DB, Houle CK. Statistical power and sample size estimation for headache research: An overview and power calculation tools. Headache. 2005;45:414–8. - PubMed
-
- Fitzner K, Heckinger E. Sample size calculation and power analysis: a quick review. Diabetes Educ. 2010;36:701–7. - PubMed
-
- Detskey AS, Sackett DL. When was a negative clinical trial big enough? How many patients you needed depends on what you found. Arch Intern Med. 1985;145:709–12. - PubMed
-
- Livingston EH, Cassidy L. Statistical power and estimation of the number of required subjects for a study based on the t-test. J Surg Res. 2005;126:149–59. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
