Cellular Response to Ionizing Radiation: A MicroRNA Story
- PMID: 24551775
- PMCID: PMC3920513
Cellular Response to Ionizing Radiation: A MicroRNA Story
Abstract
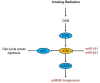
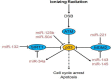
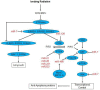
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent a class of small non-coding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. They play a crucial role in diverse cellular pathways. Ionizing radiation (IR) is one of the most important treatment protocols for patients that suffer from cancer and affects directly or indirectly cellular integration. Recently it has been discovered that microRNA-mediated gene regulation interferes with radio-related pathways in ionizing radiation. Here, we review the recent discoveries about miRNAs in cellular response to IR. Thoroughly understanding the mechanism of miRNAs in radiation response, it will be possible to design new strategies for improving radiotherapy efficiency and ultimately cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cellular response; ionizing radiation; microRNA.
Figures

References
-
- Warters RL, Hofer KG. Radionuclide toxicity in cultured mammalian cells. Elucidation of the primary site for radiation-induced division delay. Radiat Res. 1977;69:348–58. - PubMed
-
- Spitz DR, Azzam EI, Li JJ, et al. Metabolic oxidation/reduction reactions and cellular responses to ionizing radiation: a unifying concept in stress response biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23:311–22. - PubMed
-
- Wiemer EAC. The role of microRNAs in cancer: No small matter. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43:1529–44. - PubMed
-
- Rigoutsos I. New Tricks for Animal MicroRNAs: Targeting of Amino Acid Coding Regions at Conserved and Nonconserved Sites. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3245–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
