Adalimumab ameliorates abdominal aorta cross clamping which induced liver injury in rats
- PMID: 24551855
- PMCID: PMC3914326
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/907915
Adalimumab ameliorates abdominal aorta cross clamping which induced liver injury in rats
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the possible protective effects of adalimumab (ADA) on cell damage in rat liver tissue during ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury of infrarenal abdominal aorta. Thirty male Wistar-albino rats were divided into three groups: control, I/R, and I/R+ADA, each group containing 10 animals. Laparotomy without I/R injury was performed in the control group animals. Laparotomy in the I/R group was followed by two hours of infrarenal abdominal aortic cross ligation and then two hours of reperfusion. ADA (50 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally as a single dose, to the I/R+ADA group, five days before I/R. The tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (pg/mg protein) and nitric oxide (NO) (µmol/g protein) levels in the I/R group (430.8 ± 70.1, 8.0 ± 1.1, resp.) were significantly higher than those in the I/R+ADA group (338.0 ± 71.6, P = 0.006; 6.3 ± 1.2, P = 0.008) and the control group (345.5 ± 53.3, P = 0.008; 6.5 ± 1.5, P = 0.010, resp.). I/R causes severe histopathological injury to the liver tissue, but ADA leads to much less histopathological changes. ADA treatment significantly decreased the severity of liver I/R injury. ADA pretreatment may have protective effects on experimental liver injury.
Figures
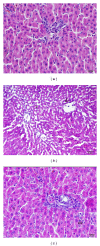
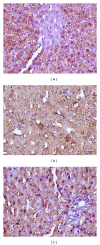

Similar articles
-
Topiramate ameliorates abdominal aorta cross-clamping induced liver injury in rats.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep-Oct;20(5):297-303. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.141690. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25253365 Free PMC article.
-
Is adalimumab protective in ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung?Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 Nov;18(11):1093-9. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26949496 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effect of Adalimumab on Renal Injury in a Model of Abdominal Aorta Cross-Clamping.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2016 Mar-Apr;25(2):219-26. doi: 10.17219/acem/33250. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27627553
-
Role of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor on lung injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion of the lower extremities.J Vasc Surg. 1997 Oct;26(4):647-56. doi: 10.1016/s0741-5214(97)70065-x. J Vasc Surg. 1997. PMID: 9357467
-
Gender differences in hepatic ischemic reperfusion injury in rats are associated with endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jun 14;11(22):3441-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3441. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15948251 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Can adalimumab prevent from acute effects of lipopolysaccharide induced renal injury in rats?Acta Cir Bras. 2024 Sep 2;39:e394624. doi: 10.1590/acb394624. eCollection 2024. Acta Cir Bras. 2024. PMID: 39230094 Free PMC article.
-
Topiramate ameliorates abdominal aorta cross-clamping induced liver injury in rats.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep-Oct;20(5):297-303. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.141690. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25253365 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:186908. doi: 10.1155/2015/186908. Epub 2015 May 12. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26064416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic Conditioning: A Potential Perioperative Strategy to Reduce Abdominal Aortic Occlusion-Related Injury in Mouse Proximal and Distal Organs.Aging Dis. 2024 Jan 24;15(6):2863-2879. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0121. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38300647 Free PMC article.
-
Is adalimumab protective in ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung?Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 Nov;18(11):1093-9. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26949496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oyar EÖ, Kiriş I, Gülmen Ş, et al. Adrenomedullin attenuates aortic cross-clampinginduced myocardial injury in rats. The American Journal of Surgery. 2011;201(2):226–232. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Zhu FX, Zhang HB, Li H, An YZ. Pretreatment with interleukin-33 reduces warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Chinese Medical Journal. 2013;126(10):1855–1859. - PubMed
-
- Trocha M, Merwid-Ląd A, Sozański T, et al. Influence of ezetimibe on ADMA-DDAH-NO pathway in rat liver subjected to partial ischemia followed by global reperfusion. Pharmacological Reports. 2013;65(1):122–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

