Emergence of community-acquired adenovirus type 55 as a cause of community-onset pneumonia
- PMID: 24551881
- PMCID: PMC7094559
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.13-1186
Emergence of community-acquired adenovirus type 55 as a cause of community-onset pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Since 2008, severe cases of emerging human adenovirus (HAdV) type 55 (HAdV-55) were reported sporadically in China. But no comparative studies had been conducted to discern the differences in epidemiologic and clinical abnormalities between HAdV-55 and other types (HAdV-7, HAdV-3, HAdV-14, HAdV-50, and HAdV-C).
Methods: A multicenter surveillance study for adult and adolescent community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) was conducted prospectively in Beijing and Yan Tai between November 2010 and April 2012. A standardized data form was used to record clinical information. The viral DNA extracted from the clinical samples or adenovirus viral isolates was sequenced.
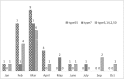
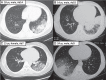
Results: Among 969 cases, 48 (5%) were identified as adenovirus pneumonia. Six branches were clustered: HAdV-55 in 21, HAdV-7 in 11, HAdV-3 in nine, HAdV-14 in four, HAdV-50 in two, and HAdV-C in one. Most HAdV-55 cases were identified during February and March. All the hypervariable regions of the hexon genes of the 21 HAdV-55 strains were completely identical. Patients who had HAdV-55 were about 10 years older ( P = .027) and had higher pneumonia severity index scores ( P = .030) compared with those with other types (HAdV-7, HAdV-3, HAdV-14, HAdV-50, and HAdV-C). Systemic BP was also higher among patients in the HAdV-55 group ( P = .006). Unilateral or bilateral consolidations were the most common radiologic findings in both patients with HAdV-55 and those with other types (57.9% vs 36%). More than one-half of the patients were admitted to hospital; oxygen therapy was given to 29.2% of the 48 patients, and two needed mechanical ventilation.
Conclusions: HAdV-55 has established itself as a major pneumonia pathogen in the Chinese population, and further surveillance and monitoring of this agent as a cause of CAP is warranted.
Figures
References
-
- Woodhead M. Community-acquired pneumonia in Europe: causative pathogens and resistance patterns. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2002;36:20s–27s. - PubMed
-
- Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, Infectious Diseases Society of America, American Thoracic Society Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(suppl 2):S27–S72. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jennings LC, Anderson TP, Beynon KA. Incidence and characteristics of viral community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Thorax. 2008;63(1):42–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

