The role of LDH serum levels in predicting global outcome in HCC patients treated with sorafenib: implications for clinical management
- PMID: 24552144
- PMCID: PMC3930857
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-110
The role of LDH serum levels in predicting global outcome in HCC patients treated with sorafenib: implications for clinical management
Abstract
Background: In many tumour types serumlactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels proved to represent an indirect marker of tumour hypoxia, neo-angiogenesis and worse prognosis. As we previously reported LDH is an important predictive factor in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Sorafenib represents the therapeutic stronghold in advanced HCC patients. As a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) mainly directed against the angiogenetic pathway, the correlation of sorafenib administration with markers of hypoxia could be an important tool in patients management. Aim of our analysis was to evaluate the role of LDH pre-treatment levels and its variation during treatment in HCC patients receiving sorafenib.
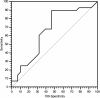
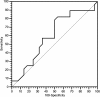
Methods: 78 patients were available for our analysis. For all patients LDH values were collected within one month before the start of treatment and after the end of therapy. For study purposes we divided our patients into two groups, according to LDH pre-treatment levels, cut-off levels was determined with ROC curve analysis. Patients were, also, classified according to the variation in LDH serum levels pre- and post-treatment (increased vs decreased).
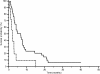
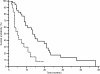
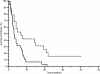
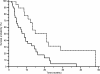
Results: Patients proved homogeneous for all clinical characteristics analyzed. In patients with LDH values under the cut-off median progression free survival (PFS) was 6.7 months, whereas it was 1.9 months in patients above the cut-off (p = 0.0002). Accordingly median overall survival (OS) was 13.2 months and 4.9 months (p = 0.0006). In patients with decreased LDH values after treatment median PFS was 6.8 months, and median OS was 21.0 months, whereas PFS was 2.9 months and OS 8.6 months in patients with increased LDH levels (PFS: p = 0.0087; OS: p = 0.0035).
Conclusions: In our experience, LDH seemed able to predict clinical outcome in terms of PFS and OS for HCC patients treated with sorafenib. Given the correlation between LDH levels and tumour angiogenesis we can speculate that patients with high LDH pretreatment levels may be optimal candidates for other emerging therapeutic agents or strategies targeting different molecular pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lactate dehydrogenase is a prognostic indicator in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by sorafenib: results from the real life practice in HBV endemic area.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 27;7(52):86630-86647. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13428. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27880930 Free PMC article.
-
The role of LDH serum levels in predicting global outcome in HCC patients undergoing TACE: implications for clinical management.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32653. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032653. Epub 2012 Mar 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22461886 Free PMC article.
-
The value of lactate dehydrogenase serum levels as a prognostic and predictive factor for advanced pancreatic cancer patients receiving sorafenib.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):35087-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5197. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26397228 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early predictive value of circulating biomarkers for sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022 Mar;22(3):361-378. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2022.2049248. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022. PMID: 35234564 Review.
-
Decade in review-hepatocellular carcinoma: HCC-subtypes, stratification and sorafenib.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Nov;11(11):645-7. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.157. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 25245016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deteriorated portal flow may cause liver failure in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma being treated with sorafenib.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016 Jun;7(3):E36-40. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2015.10.07. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27284486 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Role of a New Index (RAPID Index) in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Receiving Sorafenib: Training and Validation Cohort.Gastrointest Tumors. 2019 Oct;6(3-4):71-80. doi: 10.1159/000501593. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Gastrointest Tumors. 2019. PMID: 31768351 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation between LDH serum levels and clinical outcome in advanced biliary tract cancer patients treated with first line chemotherapy.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 11;6:24136. doi: 10.1038/srep24136. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27063994 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism as a New Avenue for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 13;24(4):3710. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043710. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential immuno-stimulating effect of curcumin, piperine, and taurine combination in hepatocellular carcinoma; a pilot study.Discov Oncol. 2023 Sep 13;14(1):169. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00785-1. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37704828 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

