dAcsl, the Drosophila ortholog of acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 3 and 4, inhibits synapse growth by attenuating bone morphogenetic protein signaling via endocytic recycling
- PMID: 24553921
- PMCID: PMC6608520
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3547-13.2014
dAcsl, the Drosophila ortholog of acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 3 and 4, inhibits synapse growth by attenuating bone morphogenetic protein signaling via endocytic recycling
Abstract
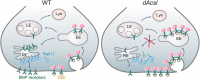
Fatty acid metabolism plays an important role in brain development and function. Mutations in acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4), which converts long-chain fatty acids to acyl-CoAs, result in nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. ACSL4 is highly expressed in the hippocampus, a structure critical for learning and memory. However, the underlying mechanism by which mutations of ACSL4 lead to mental retardation remains poorly understood. We report here that dAcsl, the Drosophila ortholog of ACSL4 and ACSL3, inhibits synaptic growth by attenuating BMP signaling, a major growth-promoting pathway at neuromuscular junction (NMJ) synapses. Specifically, dAcsl mutants exhibited NMJ overgrowth that was suppressed by reducing the doses of the BMP pathway components, accompanied by increased levels of activated BMP receptor Thickveins (Tkv) and phosphorylated mothers against decapentaplegic (Mad), the effector of the BMP signaling at NMJ terminals. In addition, Rab11, a small GTPase involved in endosomal recycling, was mislocalized in dAcsl mutant NMJs, and the membrane association of Rab11 was reduced in dAcsl mutant brains. Consistently, the BMP receptor Tkv accumulated in early endosomes but reduced in recycling endosomes in dAcsl mutant NMJs. dAcsl was also required for the recycling of photoreceptor rhodopsin in the eyes, implying a general role for dAcsl in regulating endocytic recycling of membrane receptors. Importantly, expression of human ACSL4 rescued the endocytic trafficking and NMJ phenotypes of dAcsl mutants. Together, our results reveal a novel mechanism whereby dAcsl facilitates Rab11-dependent receptor recycling and provide insights into the pathogenesis of ACSL4-related mental retardation.
Keywords: BMP signaling; Drosophila; mental retardation; neuromuscular junction; synapse; vesicle trafficking.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drosophila Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 regulates axonal transport of synaptic vesicles and is required for synaptic development and transmission.J Neurosci. 2011 Feb 9;31(6):2052-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3278-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21307243 Free PMC article.
-
Acsl, the Drosophila ortholog of intellectual-disability-related ACSL4, inhibits synaptic growth by altered lipids.J Cell Sci. 2016 Nov 1;129(21):4034-4045. doi: 10.1242/jcs.195032. Epub 2016 Sep 21. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27656110
-
AP2 Regulates Thickveins Trafficking to Attenuate NMJ Growth Signaling in Drosophila.eNeuro. 2022 Oct 12;9(5):ENEURO.0044-22.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0044-22.2022. Print 2022 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 36180220 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestrating development and function: retrograde BMP signaling in the Drosophila nervous system.Trends Neurosci. 2004 Mar;27(3):143-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2004.01.004. Trends Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15036879 Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
Cited by
-
Rosy Beginnings: Studying Peroxisomes in Drosophila.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 25;8:835. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00835. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32984330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACSL4 as a Potential Target and Biomarker for Anticancer: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Therapeutics.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 13;13:949863. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.949863. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35910359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell death inhibitors protect against brain damage caused by cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Oct 23;7(1):312. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00698-4. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34689160 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical staining reveals differential expression of ACSL3 and ACSL4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic gastrointestinal metastases.Biosci Rep. 2020 Apr 30;40(4):BSR20200219. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200219. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32286604 Free PMC article.
-
MAN1 Restricts BMP Signaling During Synaptic Growth in Drosophila.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Aug;37(6):1077-1093. doi: 10.1007/s10571-016-0442-4. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27848060 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
